FIG 1.
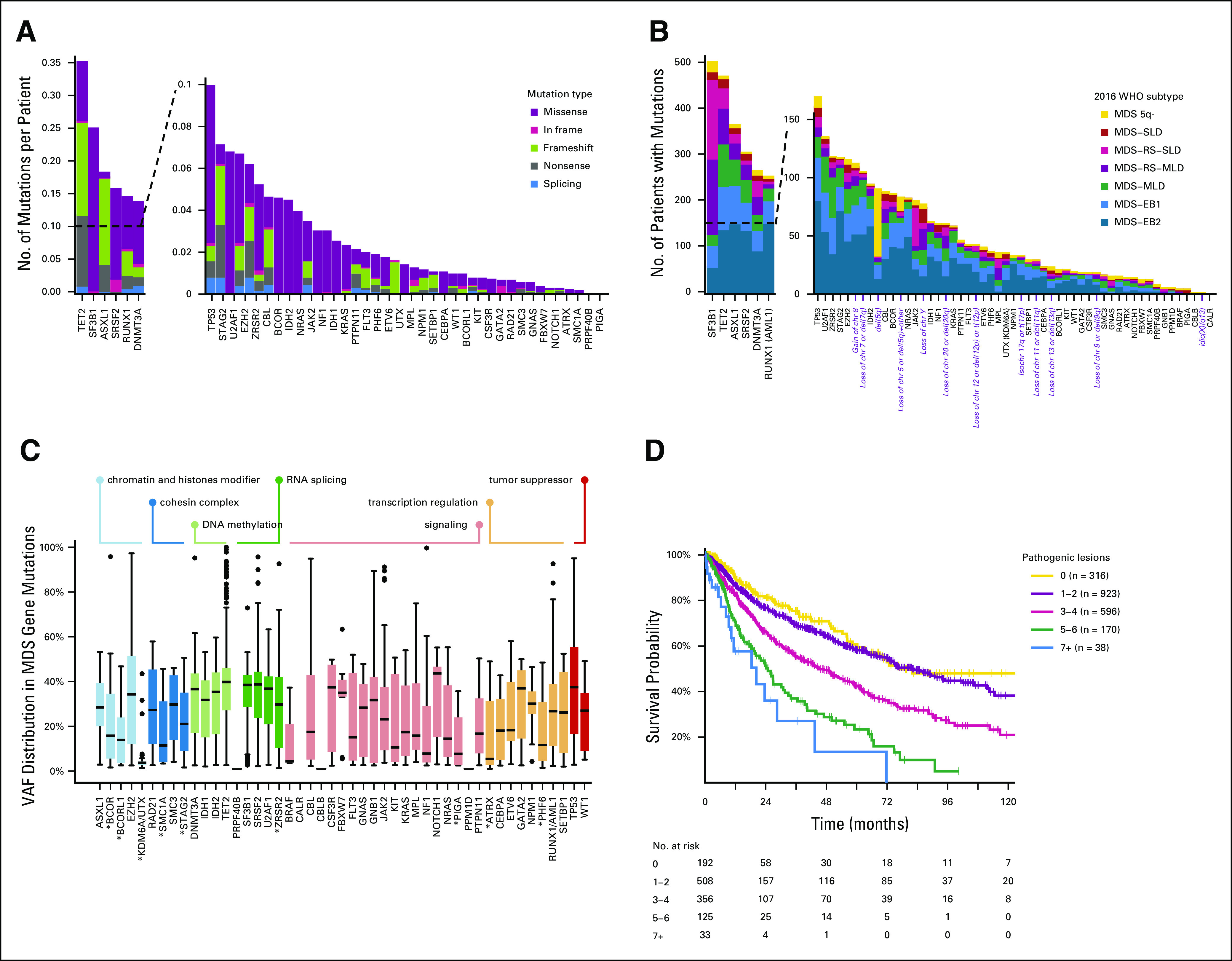
(A) Frequency of mutations and chromosomal abnormalities in the EuroMDS cohort (N = 2,043), stratified according to the type of mutation (missense, nonsense, affecting a splice site, or other). Insertions and deletions (del) were categorized according to whether they resulted in a shift in the codon reading frame (by either 1 or 2 base pairs [bp]) or were in frame. Splicing factor genes were the most frequently mutated (49%), followed by DNA methylation–related genes (37.9%), chromatin and histone modifier genes (31.3%), signaling genes (28.5%), transcription regulation genes (24%), tumor suppressor genes (11.1%), and cohesin complex genes (7.6%). (B) Frequency of recurrently mutated genes and chromosomal abnormalities in the EuroMDS cohort, broken down by MDS subtype according to 2016 WHO criteria. (C) VAF of driver mutations in the EuroMDS cohort, broken down by gene and gene function (boxplots reporting median, 25-75 percentiles, and ranges); VAF of X-linked genes (ATRX, BCOR, BCORL1, PHF6, PIGA, SMC1A, STAG2, UTX, and ZRSR2, highlighted by asterisk in the figure plot) was halved in male patients. (D) Relationship between the number of genomic abnormalities (mutations and chromosomal abnormalities) and outcome (overall survival). MDS, myelodysplastic syndromes; MDS 5q-, MDS with isolated deletion of long arm of chromosome 5; MDS-EB1, MDS with excess of blasts, type 1; MDS-EB2, MDS with excess of blasts, type 2; MDS-MLD, MDS with multilineage dysplasia; MDS-RS-MLD, MDS with ring sideroblasts and multilineage dysplasia; MDS-RS-SLD, MDS with ring sideroblasts and single-lineage dysplasia; MDS-SLD, MDS with single-lineage dysplasia; VAF, variant allele frequencies.
