Figure 1.
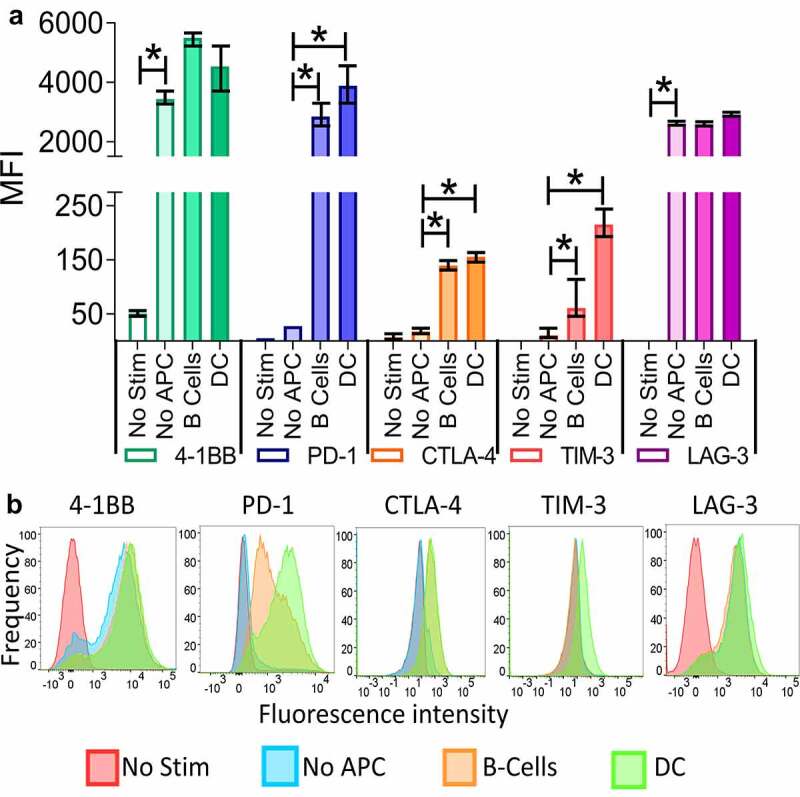
T-cell activation by professional APCs can lead to distinct immune checkpoint expression on CD8 + T cells. Splenocytes were prepared from the spleens of OT-1 mice and separated into T cells (CD8+) and B-cells (CD19+) using MACS. DC (CD11c+) were prepared from the spleens of Flt3 ligand–treated B6 mice. T cells were stimulated with a control peptide (No Stim), the SIINFEKL peptide alone (No APC), or the SIINFEKL peptide in combination with either B cells or DC. After 72 hours the cells were collected and the checkpoint and 4–1BB expression analyzed by flow cytometry. Shown is the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) and standard error of the mean of 4–1BB, PD-1, CTLA-4, TIM-3, or LAG-3 on CD8 + T cells from triplicate assessments (panel A), and a representative histogram for each marker (panel B). Asterisks indicate p < .05 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons correction. Results are from one experiment (N = 3 mice per group) and are representative of two similar, independent experiments
