Figure 1.
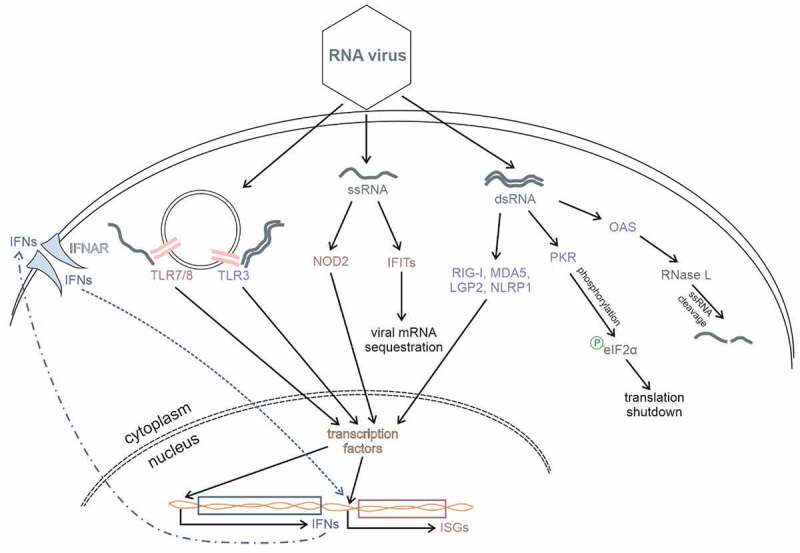
Cell signalling pathways that respond to viral RNA. During viral infection vRNA, single- or double-stranded, is introduced into the cell. This RNA is recognized by cellular sensors, RIG-I, MDA5, LGP2, PKR, OAS, TLR3/7/8, NLRP1, NOD2, and IFITs. Upon vRNA sensing, type I interferon response, as well as the production of antiviral IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), is activated. Moreover, some vRNA sensors exert their function directly on viral RNA either by sequestrating viral transcripts from the pool of translationally active mRNAs (IFIT proteins) or by stimulating RNase L to degrade RNAs (OAS). Activation of PKR leads to phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2α what subsequently results in global translation shutdown
