Figure 3.
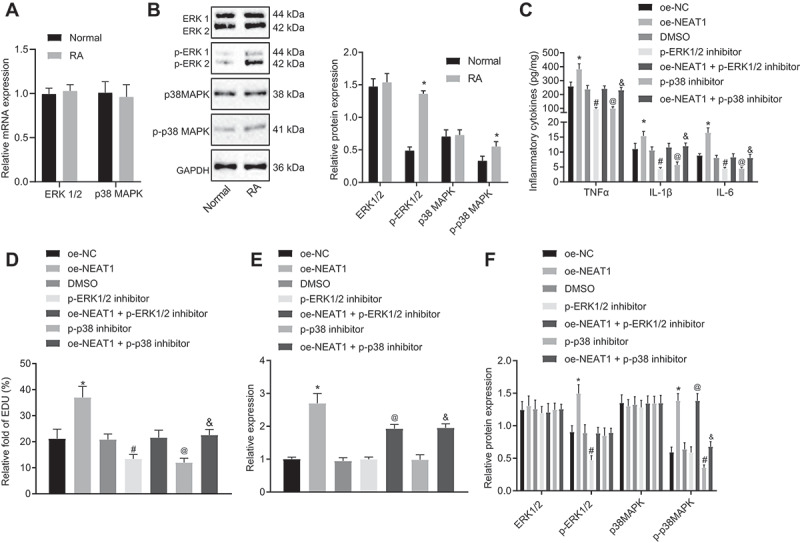
Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 suppresses FLS proliferation and synovitis through inactivation of the MAPK/ERK signalling pathway. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of ERK1/2 expression in synovial tissues of normal control subjects and patients with RA. (B) Western blot analysis of ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK expression and phosphorylation level of ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK normalized to GAPDH in synovial tissues of normal control subjects and patients with RA. * p < 0.05 vs. normal synovial tissues. (C) ELISA assays for TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels in FLS upon lncRNA NEAT1 overexpression and MAPK/ERK inhibition. (D) FLS proliferation upon lncRNA NEAT1 overexpression and MAPK/ERK inhibition determined by EdU assay. (E) RT-qPCR determination of lncRNA NEAT1 and ERK1/2 expression after lncRNA NEAT1 overexpression and MAPK/ERK inhibition in FLSs. (F) Western blot analysis of ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK expression and extent of ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK phosphorylation normalized to GAPDH in FLSs after lncRNA NEAT1 overexpression and MAPK/ERK inhibition. * p < 0.05 vs. the oe-NC treatment; # p < 0.05 vs. the DMSO treatment, @ p < 0.05 vs. the phosphorylated ERK1/2 inhibitor, & p < 0.05 vs. the phosphorylated P38 inhibitor. The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analysed using one-way analysis of variance. The experiment was repeated three times independently
