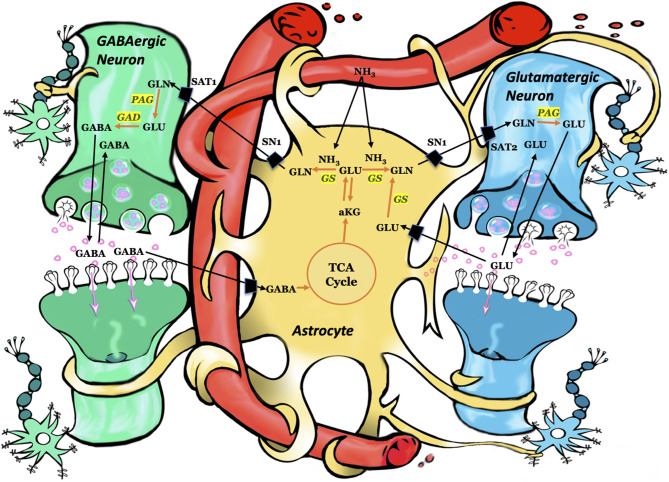
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of key pathways involving astrocytes, glutamatergic neurons, and GABAergic neurons. Each arrow signifies several reactions. Using ammonia, glutamine synthetase converts glutamate to glutamine. Subsequently, glutamine is taken up by the adjacent neurons and converted to glutamate or GABA. Astrocytes take up the synaptic glutamate (glutamine–glutamate cycle) or GABA (glutamine–glutamate–GABA cycle) and converts these neurotransmitters to glutamine via glutamine synthetase. GLN, glutamine; GLU, glutamate; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; aKG, alpha ketoglutarate; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; GS, glutamine synthetase; PAG, phosphate-activated glutaminase; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; SN1, system N transporter 1; SAT1, system A transporter and SAT2, system A transporter 2. Figure adapted with permission from (43).