Figure 2.
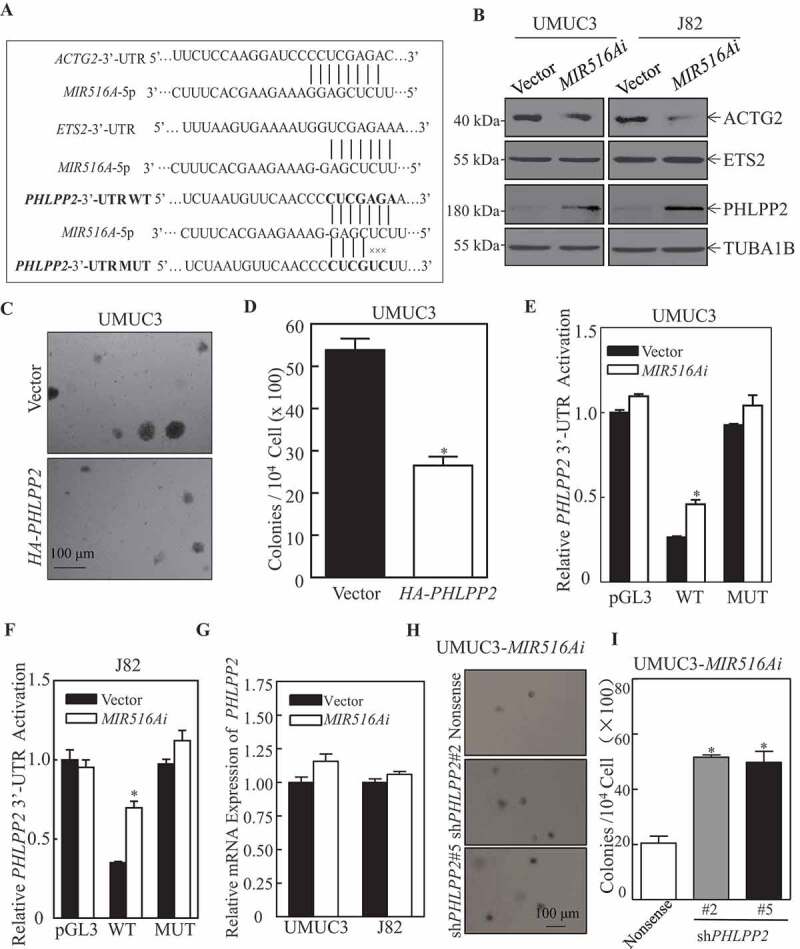
MIR516A bound to the 3′-UTR of PHLPP2 mRNA and downregulated its protein expression in human BC cells. (A) Potential MIR516A targeting sequences in the 3′-UTR of PHLPP2, ACTG2, and ETS2 mRNAs as identified by using TargetScan; and the mutation constructs of potential MIR516A binding sites of 3ʹ-UTR of PHLPP2. (B) The protein expression of ACTG2, ETS2, and PHLPP2 in UMUC3 and J82 cells were determined by western blotting in cells overexpressing the MIR516A inhibitor. (C and D) A soft agar assay was employed to determine the effect of PHLPP2 overexpression on UMUC3 anchorage-independent growth and the images were captured under microscopy (C); the number of colonies was counted and presented as colonies per 10,000 cells (D). (E and F) pGL3, wild-type and mutant of PHLPP2 3′-UTR mRNA luciferase reporters together with pRL-TK were transiently co-transfected into the indicated cells. The luciferase activity of each transfectant was evaluated, and the results were shown as relative pGL3 activity. The results were expressed as the mean ± SD obtained from the triplicates (*p < 0.05). (G) The indicated cells were extracted for total RNA with TRIzol reagent. qPCR was used to determine PHLPP2 mRNA expression. (H and I) The effects of PHLPP2 knockdown in MIR516Ai-expressed UMUC3 cells by a soft agar assay, representative images of colonies of the indicated cells were acquired under a microscope (H). (I) The results are expressed as the mean ± SD, and asterisks indicate a significant increase compared with nonsense control transfectants (*p < 0.05)
