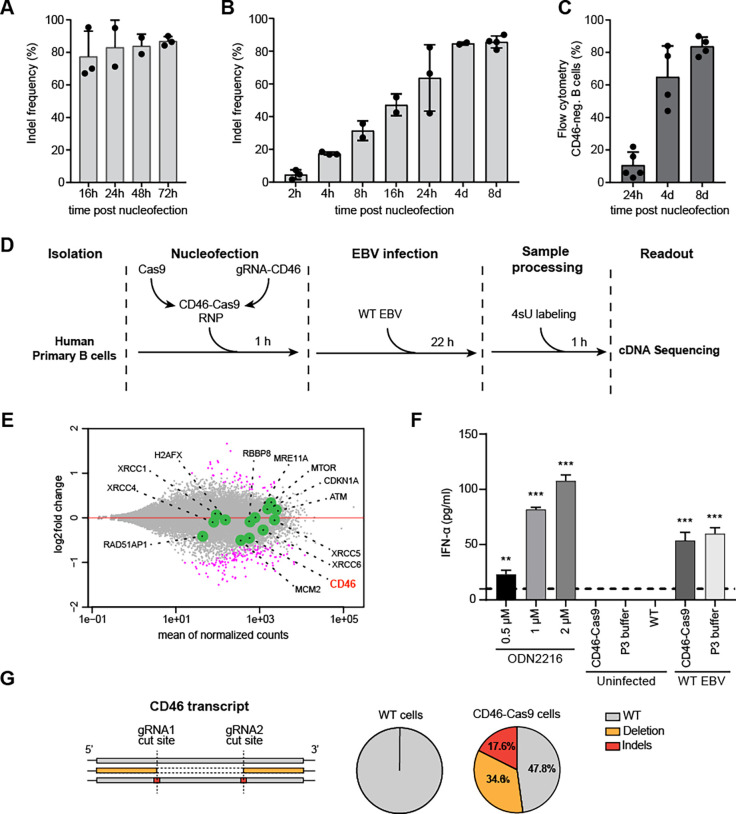
Fig 2. The kinetics of induced DNA breaks and their repair in the second exon of CD46 in non-infected and EBV-infected primary human B cells.
(A) Primary human B cells were nucleofected with the two CD46-Cas9 RNP complexes and analyzed 16, 24, 48 and 72 hours later. The cells were left non-infected. At the indicated time points viable cells were selected by Ficoll gradient centrifugation. Part of the CD46 locus in their cellular DNA was amplified in a two level PCR barcoding scheme prior to next generation sequencing. Data were analyzed using the Outknocker 2.0 web tool. The results showed a indel frequency of 70% in primary human B cells 16 h after nucleofection in the absence of EBV infection. Indel frequencies increased up to 90% 72 h after nucleofection. Mean and standard deviation of independent biological replicates are shown. (B) The time course experiments show the indel frequencies in the second exon of CD46 in EBV infected primary B cells after nucleofection with two CD46-Cas9 RNP complexes. Cellular DNA of viable cells was amplified in a two level PCR barcoding scheme prior to next generation sequencing and the data were analyzed with the Outknocker 2.0 web tool. Indel frequencies increased up to 85% 8 days after nucleofection. Mean and standard deviation of independent biological replicates are shown. (C) CD46 flow cytometry analyses of primary B cells 1, 4 and 8 days after nucleofection with two CD46-Cas9 RNP complexes and subsequent infection with WT EBV are shown. Mean and standard deviation of independent biological replicates are provided. (D) Scheme of metabolic labeling of newly transcribed RNAs with 4sU and their analysis by next generation sequencing. 2×107 primary human B cells were nucleofected with two CD46-Cas9 RNP complexes. Nucleofected (CD46-Cas9) as well as adjusted numbers of untreated (WT) B cell samples were infected with wild-type (WT) EBV. 23 hours after nucleofection, newly transcribed RNAs were metabolically labeled with 4sU for 1 hour. After RNA extraction, biotinylation of newly transcribed 4sU labeled RNAs and their enrichment, cDNA libraries were established and sequenced on a NextSeq500 (Illumina) instrument with 2x150 bp paired end reads. 15.7 to 18.6 Mio reads per sample were obtained. (E) An MA plot shows the differentially expressed genes in CD46-Cas9 vs. WT B cell samples following EBV infection and 4sU labeling 24 hours after B cell preparation. Log2-fold changes and mean of normalized read counts were plotted on the y- and x-axes, respectively. 182 differentially expressed genes are designated by magenta dots. Green dots highlight the CD46 gene and genes involved in the different pathways of DNA repair. Ongoing transcription at the CD46 locus was intact in CD46-Cas9 RNP complex nucleofected cells but reduced by a factor of 0.73 24 h after nucleofection. (F) IFN-α release of primary B lymphocytes after RNP nucleofection. B cells nucleofected with the CD46-Cas9 RNP complexes or cells nucleofected with P3 buffer, only, were cultured with or without WT EBV infection overnight. On the next day, the cells were counted and re-seeded with identical cell numbers. After 48 hours, supernatants were collected and IFN-α was measured by ELISA. As positive controls, uninfected cells were treated with different concentration of the TLR9 agonist ODN2216 for 20 hours prior to analysis. The threshold level of detection was 10 pg/ml IFN-α as indicated by the dashed line. P values were calculated using the one-way ANOVA test. ***, P<0.001, **, P<0.01. Mean and standard deviation of two biological and technical replicates are shown. (G) Shown are three schematic examples of mapped reads aligned to the hg19 reference sequence together with the two RNP complex target sites (chr1: 207,930,419–207,930,438 and chr1: 207,930,497–207,930,516) at exon 2 of the CD46 gene. Reads with unmodified exon 2 (WT) sequences, reads with nucleotide mutations (indels, i.e. base changes or small insertions and deletions), reads with deletions in between the two annotated RNP complex target sites and their percentages are shown.