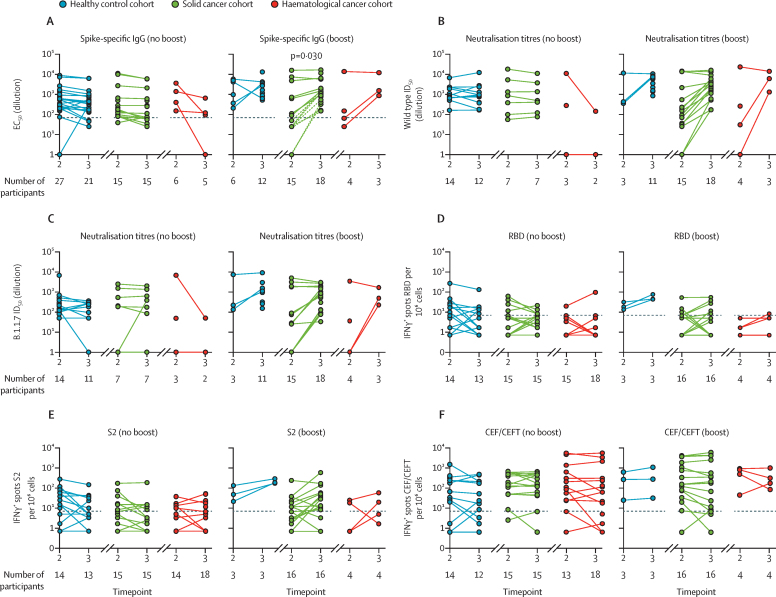
Figure 3.
Comparison of single dose versus prime–boost with COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2
(A) Spike-specific IgG titres in plasma samples at 3 and 5 weeks after the vaccine in individuals receiving a single vaccine dose (no boost) and in those receiving two doses (boost). Patients failing to achieve a serological response at any timepoint were excluded. Dashed lines represent eight non-responders with solid cancer at timepoint 2 who seroconverted following boost. (B) Neutralisation titres against wild-type SARS-CoV2 in plasma samples at 3 and 5 weeks after the vaccine in individuals receiving a single vaccine dose (no boost) and in individuals receiving two doses (boost). Patients failing to achieve a serological response at any timepoint were excluded. (C) Neutralisation titres against B.1.1.7 SARS-CoV-2 in plasma samples at 3 and 5 weeks after the vaccine in individuals receiving a single vaccine dose (no boost) and in individuals receiving two doses (boost). Patients failing to achieve a serological response at any timepoint are excluded. (D–F) Cytokine response to stimulation with peptides from RBD, S2, and CEF/CEFT reported as number of spots per 106 PBMC at 3 and 5 weeks after the vaccine in individuals receiving a single vaccine dose (no boost) and in individuals receiving two doses (boost). All comparisons tested by paired Wilcoxon test, corrected by Benjamini-Hochberg method. CEF/CEFT=cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza virus (and tetanus toxin) peptide pools. EC50=50% effective concentration. ID50=inhibitory dilution at which 50% of viral particles are neutralised. IFNγ=interferon-γ. PBMC=peripheral blood mononuclear cell. RBD=receptor binding domain. S=spike protein. S2=spike protein 2.