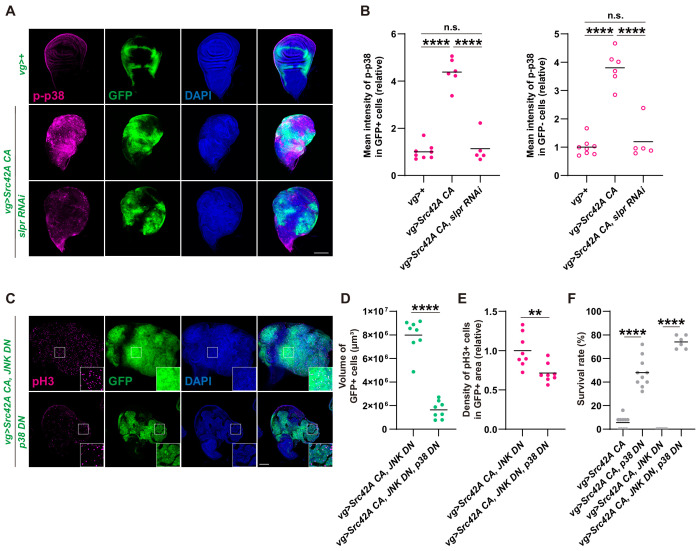
Figure 4. p38 mediates Src-induced cell proliferation.
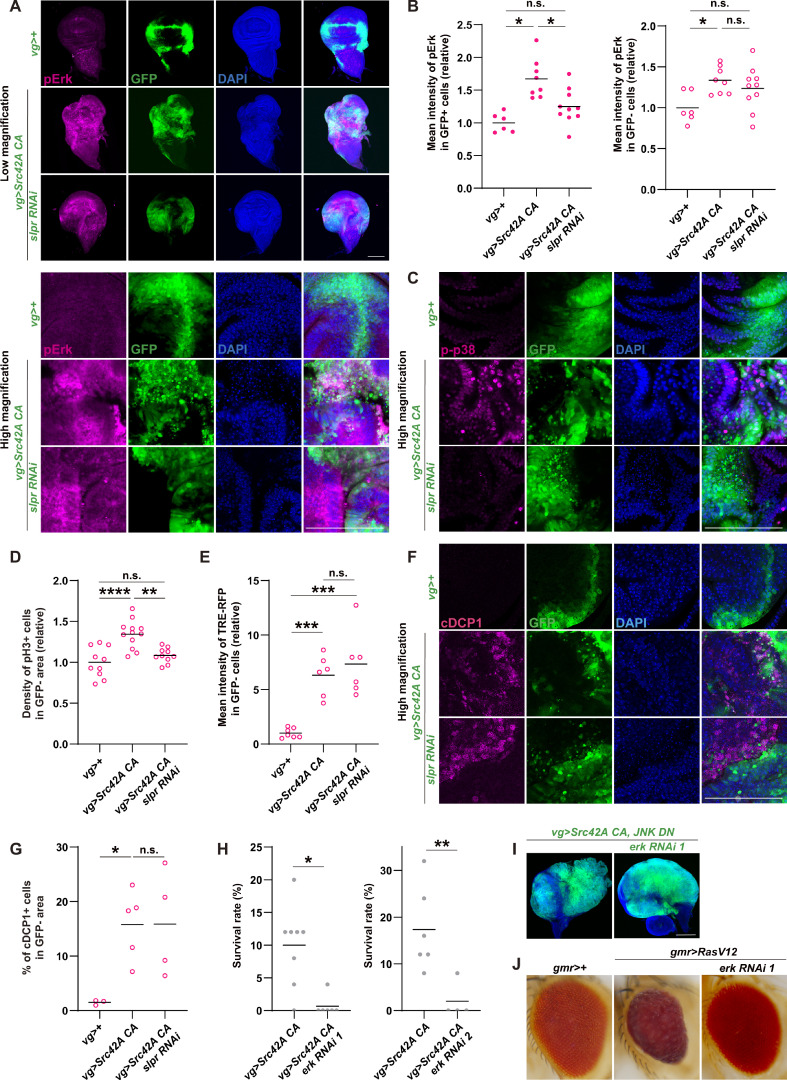
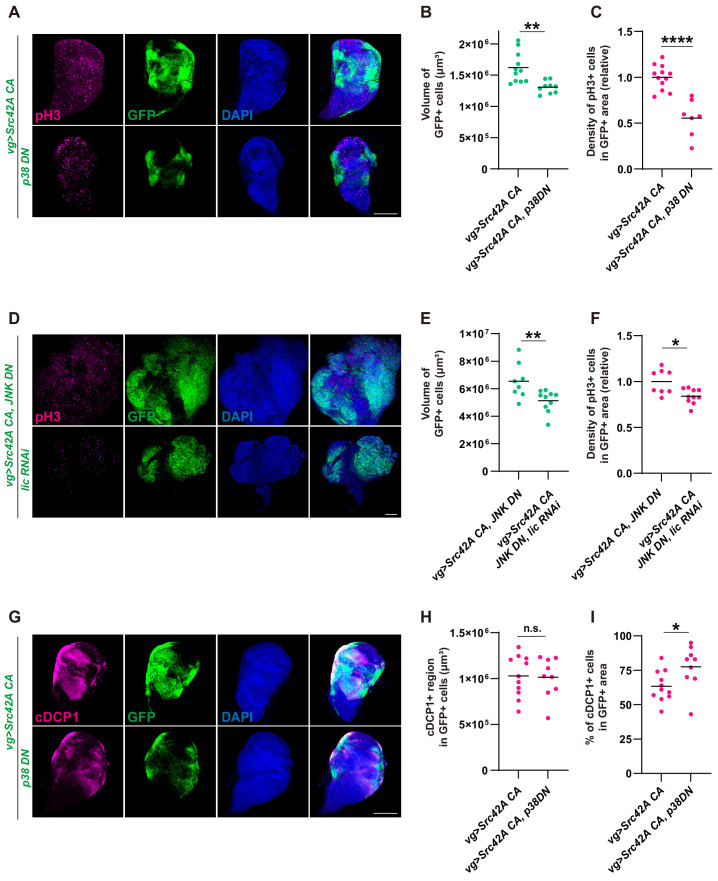
(A) Src42A constitutively active (CA) expression induces phosphorylation of p38 both cell autonomously and non-cell autonomously, which is suppressed by slpr knockdown. (B) Quantification of phosphorylated p38 in A. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. (C) Src42A CA-induced proliferation with/without JNK inhibition is suppressed by p38 DN. (D) Quantification of the total volume of GFP+ cells (µm³) in C. Two-tailed unpaired t-test. (E) Quantification of phospho-histone 3 (pH3) staining in C. The number of pH3+ cells was normalized by the area of GFP+ cells. Two-tailed unpaired t-test. (F) Inhibition of p38 suppresses organismal lethality induced by Src42A CA. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. Scale bars, 100 µm.