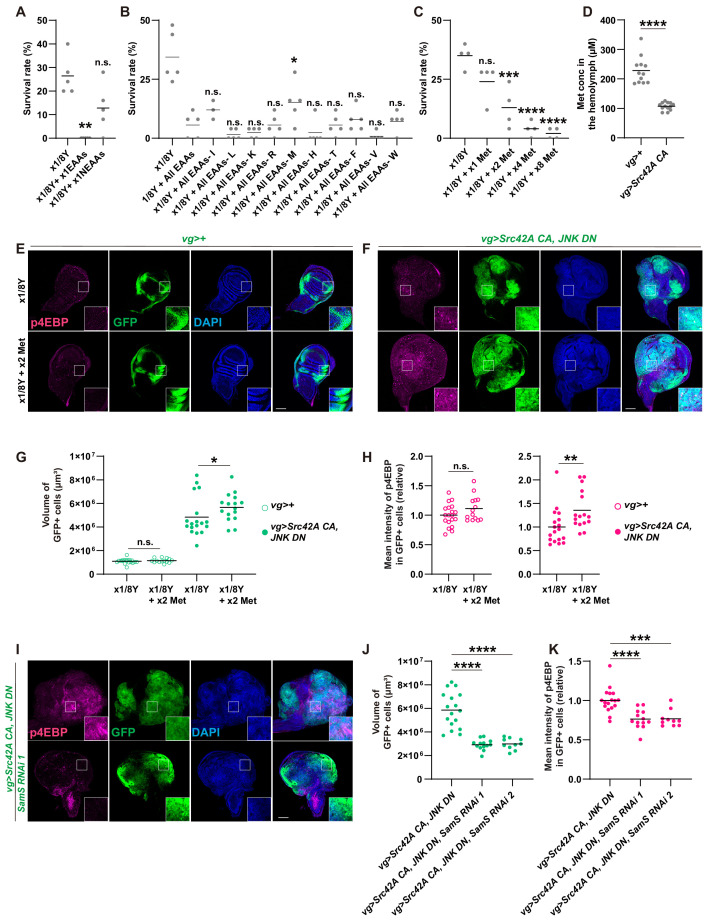
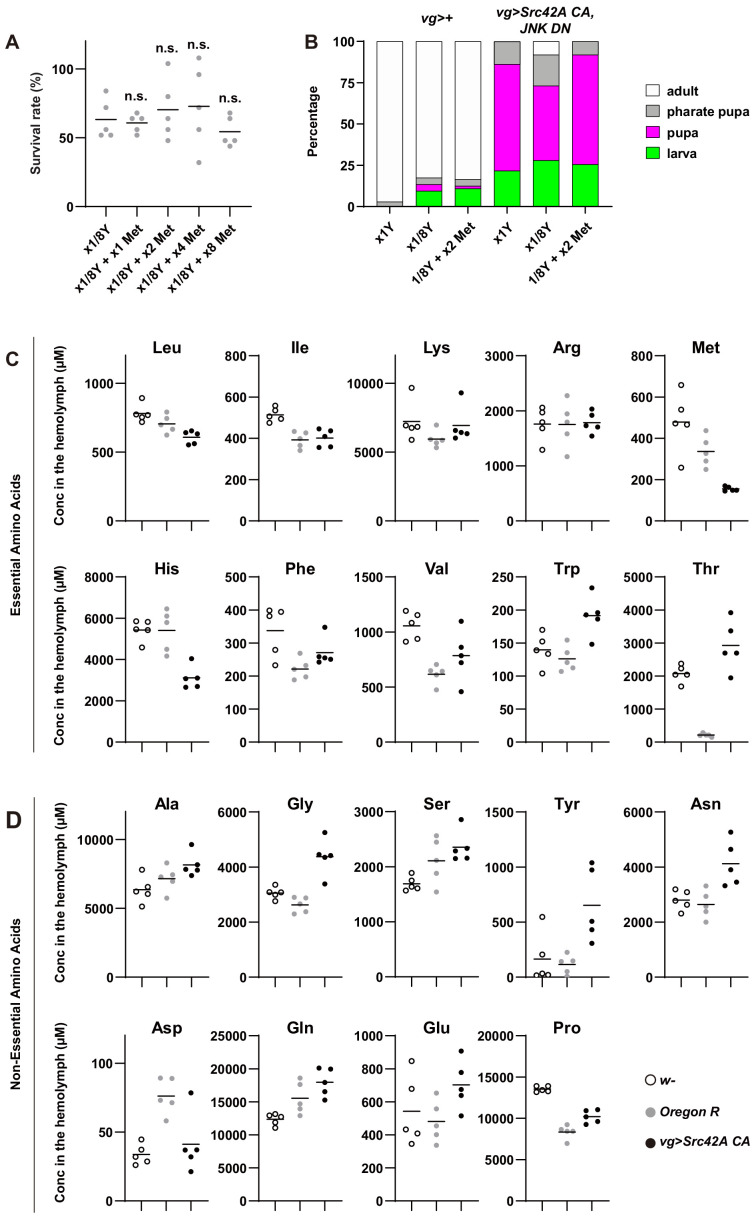
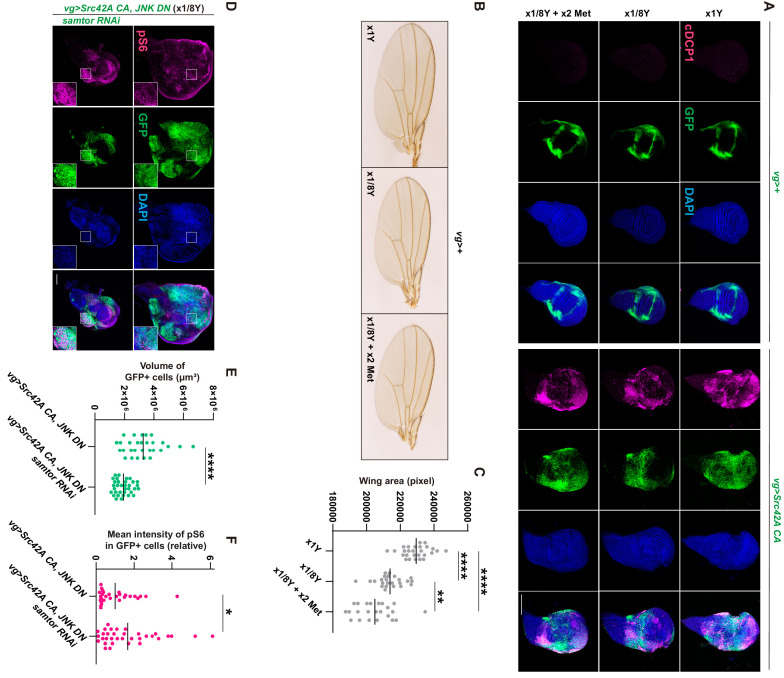
Figure 7. Methionine regulates Src-induced Tor signaling, tissue growth, and organismal lethality.
(A) Addition of essential amino acids enhances organismal lethality caused by Src42A constitutively active (CA) expression in the wing disc, whereas addition of non-essential amino acids does not. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test. (B) Only methionine subtraction from the diet improves organismal survival over the Src42A CA stress. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. (C) Addition of methionine reduces organismal survival over the Src42A CA stress in a dose-dependent manner. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. (D) An amount of methionine in the hemolymph was measured by LC-MS/MS. Expression of Src42A CA in the wing disc decreases the circulating methionine in the hemolymph. Two-tailed unpaired t-test. (E-F) Dietary methionine activates both cell proliferation and phosphorylation of 4EBP that are induced by Src42A CA and JNK DN. (G) Quantification of the total volume of GFP+ cells (µm³) in E-F. Mann-Whitney test. (H) Quantification of phosphorylated 4EBP in E-F. Two-tailed unpaired t-test. (I) SamS knockdown suppresses phosphorylation of 4EBP and overgrowth induced by Src42A CA and JNK DN. (J) Quantification of the total volume of GFP+ cells (µm³) in I. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. (K) Quantification of phosphorylated 4EBP in I. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-test. Scale bars, 100 µm.