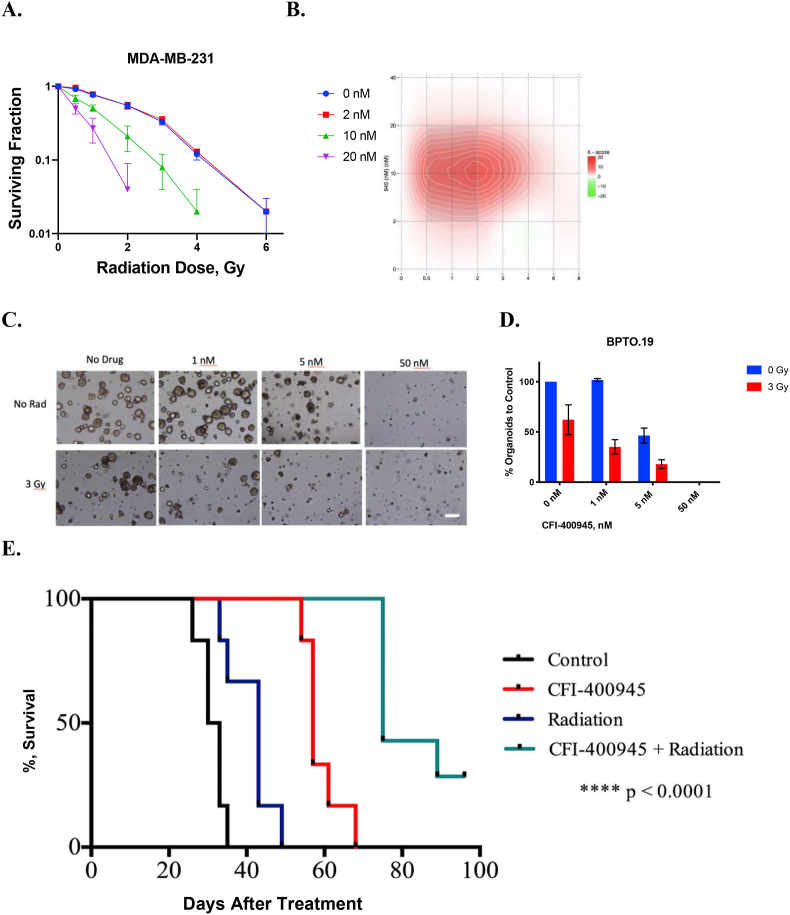
Fig. 1.
Effects of CFI-400945 and Radiation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo Models. A. Combined CFI-400945 and radiation resulted in dose-dependent reductions in colony formation in MDA-MB-231. The number of colonies in each treatment arm were normalized to the respective control (no-radiation, no-drug). B. Synergy of combined CFI-400945 and radiation was observed across several dose levels. Bliss synergy scores, calculated with SynergyFinder, are displayed in the heatmap, where intensity of red indicates higher degree of synergy. C. Organoid formation assay using various concentrations of CFI-400945 alone (top panel) or in combination with 3 Gy radiation (bottom panel) in BPTO19, generated from a chest wall metastasis of a TNBC patient. Bright-field microscopy (at 4× magnification) images were taken 28 days following treatment. The number of organoids was counted by 2 independent observers in at least 3 random fields per each well. The counts were normalized to respective unirradiated controls in each group. Bar represents 100 μm. D. Effect of CFI-400945 and radiation in BPTO19. Average number of organoids was normalized to that of control (no-radiation, no-drug). Averages and standard deviations (SD, bars) of replicate experiments are presented. E. In Vivo effects of CFI-400945 and Radiation on MDA-MB-231 Xenografts in NOD/SCID mice. Tumor endpoint survival curve (left) using Kaplan-Meier analysis. P-value was calculated using log-rank test. No significant effects on animal general health and weight were observed, and no detectable metastases (liver and lungs) were seen on the autopsy in all study arms. Significantly smaller proportion of mice developed tumor ulceration in the combination treatment arm compared to other treatment arms.