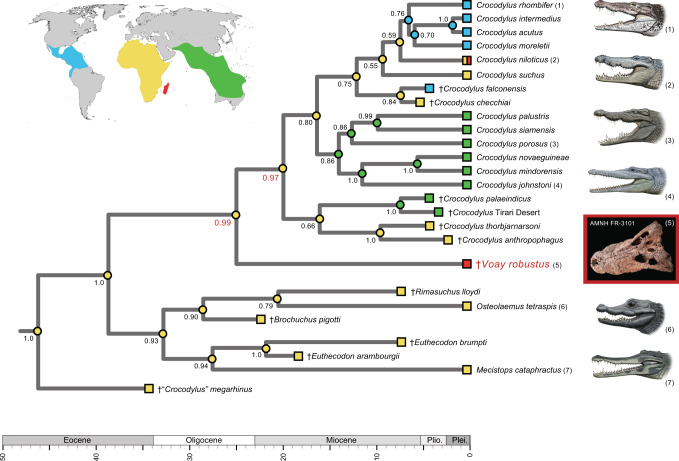
Fig. 4. Tip-dated Bayesian timetree showing the phylogenetic relationships of Voay robustus relative to extant and extinct crocodylids with a mapping of geographic distributions (colored squares at tips of branches).
Bayesian posterior probabilities are at nodes; support scores for the two internodes that bound the branching point of Voay are highlighted (red). Optimization of geographic regions to internal nodes (colored circles) is based on equally-weighted parsimony and implies an African ancestry for the overall clade with minimally two migrations to Australia/Asia, two to the New World, and two to Madagascar. An identical mapping of ancestral areas results for minimum area change (MAC) parsimony analysis. The Voay AMNH FR-3101 C. porosus mt genome build (partitioned by 1st, 2nd, 3rd codons) was employed in combination with morphological characters and stratigraphic data from Lee and Yates (2018). Taxa that are distantly related to Voay are pruned from the figure; for the complete timetree, see Supplementary Data 2. Paintings of crocodylians are by C. Buell; photo of Voay (AMNH FR-3101) is by E. Hekkala.