Fig. 2. Representative images of the retinal microvascular networks imaged using optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA).
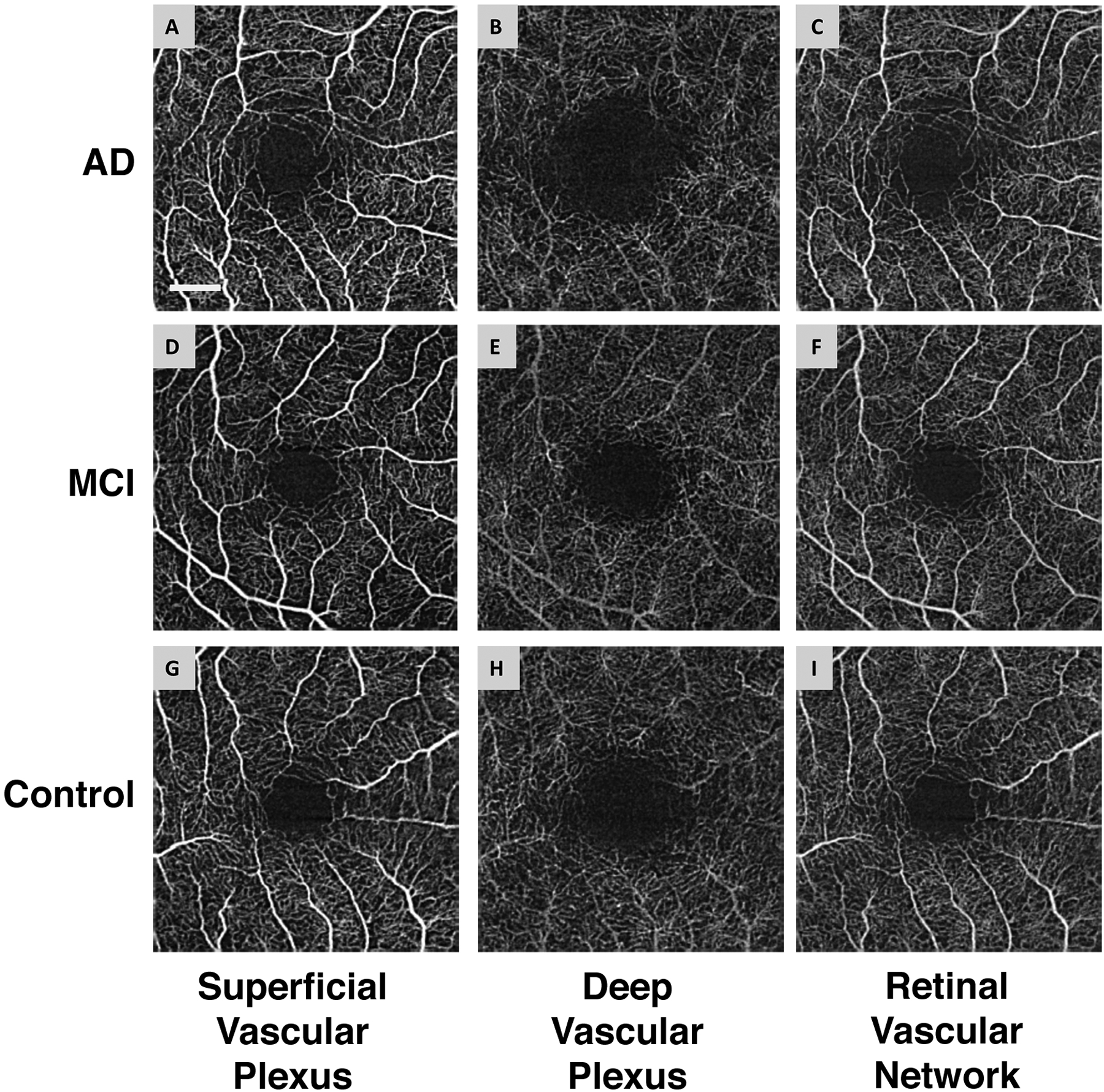
Patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (A, B, and C) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) (D, E, and F), as well as a control subject (G, H, and I), were imaged. Compared to the normal control (G and I), the large vessels in AD and MCI patients had similar densities in the superficial vascular plexus (A and D) and retinal vascular network (C and F) but showed some degrees of tortuosity. The microvessels in the deep vascular plexus in AD (B) and MCI (E) patients appeared to be less dense compared to the normal control (H). Note: the deep vascular plexus images are raw images, showing the graphic projection artifact of the large vessels. Bar = 0.5 mm. (Reproduced and used with permission obtained through RightsLink)
