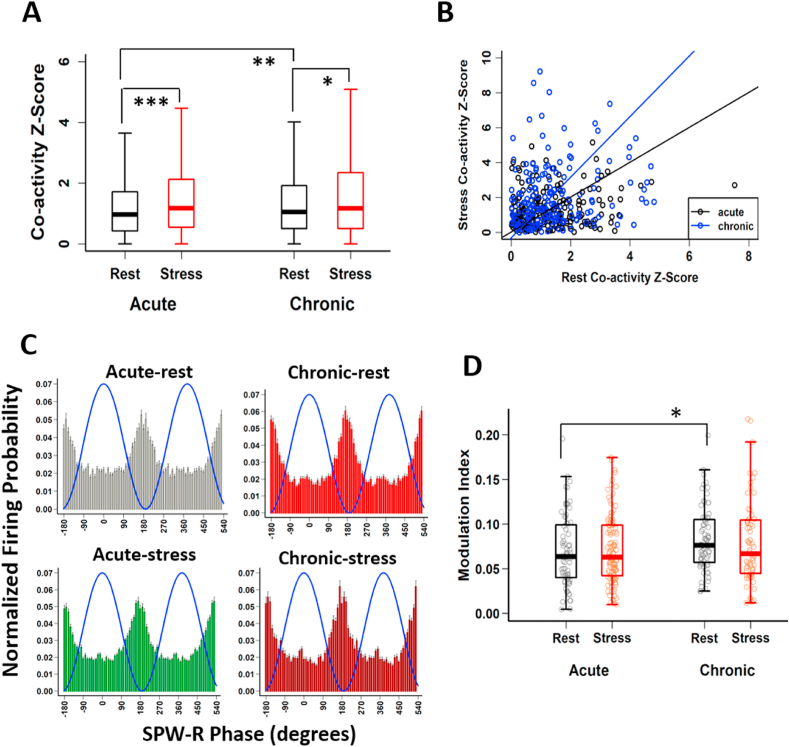
Fig. 4.
Altered CA1 pyramidal cell coactivation in SPW-Rs during stress-state. (A) Co-activity Z-scores of pyramidal cells during SPW-Rs differ between rest-state (black) and stress-state (red) (two-way ANOVA: behaviour-state, F(1, 6195) = 41.286, p = 1.41 × 10−10; day, F(1, 6195) = 4.676, p = 0.031; behaviour-state x day, F(1, 6195) = 4.861, p = 0.027; Tukey's HSD: acute-rest, n = 1625 cell pairs vs acute-stress, n = 1610 cell pairs, p = 4.04 × 10−9; chronic-rest, 1701 cell pairs vs chronic-stress, n = 1263 cell pairs, p = 0.025; acute-rest vs chronic-rest, p = 0.0035). (B) Relationship between cell pairs of positive co-activity Z-scores during both rest-state and stress-state significantly differs between days (acute: slope = 0.99, R2 = 0.022, p = 0.033 n = 208 cell pairs; chronic: slope = 1.74, R2 = 0.019, p = 0.076, n = 165 cell pairs; likelihood-ratio test, p = 1.28 × 10−7) of CIS. (C) Group histograms for pyramidal cell spiking during SPW-Rs for acute-rest (grey), acute-stress (green), chronic-rest (red) and chronic-stress (maroon). The Blue lines on each subpanel represents the phase of the SPW-R. (D) Modulation index differs slightly between days (LMMs: behaviour-state, F(1, 311) = 0.016, p = 0.900; day, F(1,311) = 6.335, p = 0.012; behaviour-state x duration, F(1, 311) = 1.294, p = 0.256; Tukey's HSD: acute rest vs chronic rest, p = 0.049). Boxplots represent interquartile range (IQR, 25th-75th percentiles), median is the thick line in the box and whiskers extend to 1.5 times the IQR. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.001. Acute-rest: N = 17 mice; acute-stress, N = 16 mice; chronic-rest, N = 16 mice; chronic-stress, N = 16 mice). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)