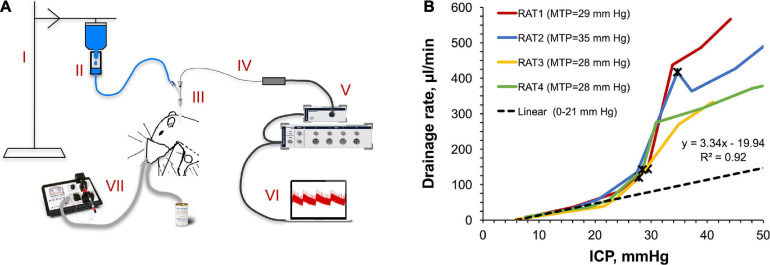
FIGURE 2.
Viability of the CSF drainage system under pressure. (A) A sketch of the originally developed experimental setup for measuring the rate of unconstrained CSF drainage at different ICPs. Components of the setup: (I) bench-top pole with a suspended saline bag set at different heights, (II) dripper with calibrated drop size attached to the saline bag and connected to the saline line, (III) Tuohy Borst adapter attached to the catheter inserted in the cisterna magna; saline line connected to the adapter’s side arm, (IV) micro-tip pressure sensor advanced to the cisterna magna through the adapter and catheter, (V) data acquisition platform, (VI) control and data analysis console (note the ICP fluctuations on the computer screen caused by falling drops), (VII) small-animal isoflurane anesthesia platform. (B) ICP dependency of the CSF drainage rate. MTP: maximally tolerated pressure. Black asterisks mark MTP for each rat. Data points in the 6–23 mm Hg region were used to build a linear regression (parameters are shown).