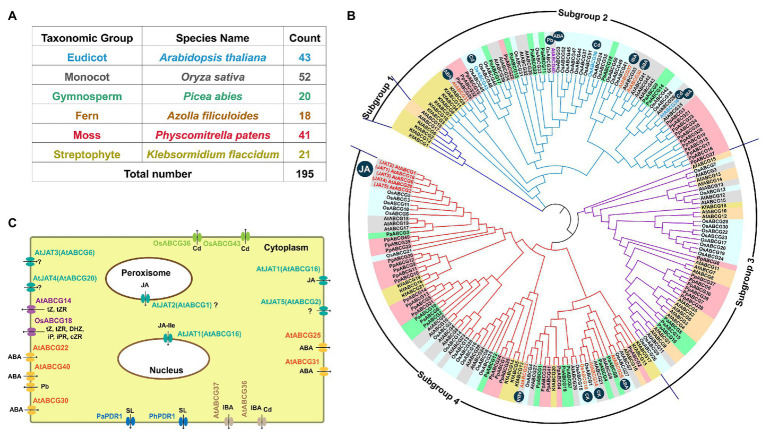
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic analysis and phytohormone transport of ATP-Binding Cassette G (ABCG) subfamily. Number (A) and phylogenetic tree (B) of ABCGs identified in six representative plant species including five land plants and a basal Streptophyte alga. Four major subgroups of ABCGs are shown by different lines. The homologs from the same organism are shaded with the same background color, except the Arabidopsis JA transporters (AtJATs). The heavy metal-responsive members including AtABCG36/40, and OsABCG36/43/44 are labeled with black symbols. (C) The known subcellular localization of functional characterized ABCGs in various plant species. ABCG homologs with are obtained from the references (Saha et al., 2015; Hwang et al., 2016; Cho et al., 2020) and databases (https://www.uniprot.org/, https://www.fernbase.org/, https://congenie.org/, and http://www.plantmorphogenesis.bio.titech.ac.jp), the phylogenetic tree is generated by using MEGA7 (Kumar et al., 2016). At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Os, Oryza sativa; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Kf, Klebsormidium flaccidum; Af, Azolla filiculoides; Pa, Picea abies; Pp, Physcomitrella patens; PhPDR1, Petunia hybrida pleiotropic drug resistance 1; tZ, trans-zeatin; tZR, trans-zeatin riboside; cZ, cis-zeatin; cZR, cis-zeatin riboside; iP, isopentenyladenine; iPR, isopentenyladenosine. SL, strigolactone; IBA, indole-3-butyric acid; ABA, abscisic acid; JA, jasmonic acid; and JA-Ile, jasmonoyl-isoleucine.