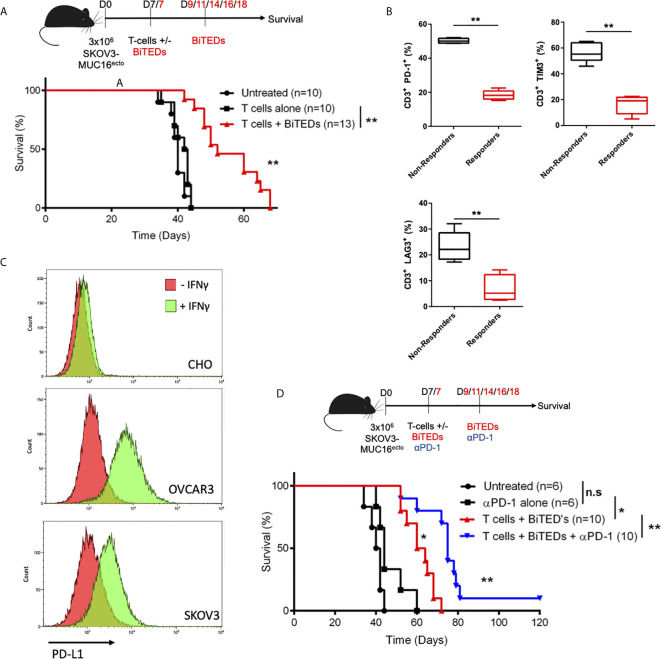
Figure 5.
MUC16ecto-BiTEDs improve overall survival in tumor-bearing mice as monotherapy and in combination with PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade. (A) NSG tumor-bearing mice were inoculated i.p. with SKOV3-MUC16ecto tumor cells and treated with either T-cells alone or T-cells and MUC16ecto-BiTEDs. Data shown are pooled results from 3 independent experiments with at least 4 independent donors. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.05. Tumor was injected on D0 i.p. T-cells were injected on D7 i.v in all animals. Animals that received BiTEDs treated were dosed i.p on D7, D9, D11, D14, D16 and D18. (B) Immunophenotyping of human T-cells from the spleens of female NSG SKOV3-MUC16ecto tumor-bearing mice treated with BiTEDs who had either succumbed to disease (Non-Responders) or from those who lived longer (Responders). **p < 0.05. (C) CHO, OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cells with or without IFN-γ stimulation for 24 hrs. Data shown representative of 2 independent experiments. (D) SKOV3-MUC16ecto tumor-bearing mice were treated with T-cells and αPD-1 alone, T-cells and BiTEDs, or T-cells, αPD-1 and BiTEDs. Tumor was injected on D0 i.p. T-cells were injected on D7 i.v in all animals. Animals that received BiTEDs treated were dosed i.p on D7, D9, D11, D14, D16 and D18. Anti-PD-1 (clone EH12.2H7) was injected i.p. on D7, D14, D21 and D28. Data shown are pooled results from 3 independent experiments with at least 4 independent donors. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 T-cells + αPD-1 vs T-cells + BiTEDs, **p < 0.05 T-cells + BiTEDs vs T-cells + BiTEDs + αPD-1. Statistical analysis for (A, C) performed using a log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. ns, not significant.