Figure 4.
The MR virus shows resistance in vivo to neutralization by MeV A-induced antibodies
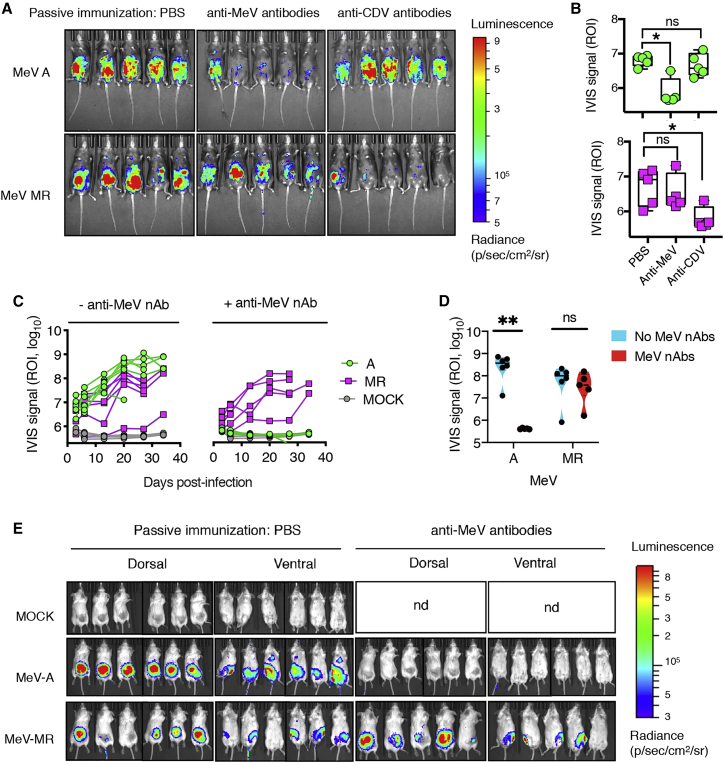
(A) Bioluminescence signal of a virally encoded firefly luciferase (Fluc) signal in Ifnar™-CD46Ge mice pre-treated or not (PBS group) with guinea pig anti-MeV or ferret anti-CDV nAb-containing serum. The images were recorded 3 days after infection and show absence of a bioluminescence signal for MeV A in the presence of MeV antibodies, whereas the presence of CDV antibodies, but not MeV antibodies, inhibited the virus MR.
(B) Quantification of the bioluminescence signal emitted from the abdominal and ventral area or region of interest (ROI) from each mouse infected with MeV in the presence or absence of passive immunity. PBS represents mock-immunized mice. ∗p < 0.005, as calculated with Dunnett’s corrected 1-way ANOVA with 12 degrees of freedom.
(C) Bioluminescence quantitative signal (photons) of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice bearing subcutaneous KAS 6/1 cells treated intravenously with one dose of the indicated rMeV(Fluc) or PBS. Mice in the relevant group also received anti-MeV antibodies (MeV-specific guinea pig antiserum) intraperitoneally 3 h before MeV injection.
(D) Comparative analysis of the bioluminescence signal was determined on day 20 for MeV A and MeV MR in the absence or presence of anti-MeV antibodies. Nd, not done. ∗∗p = 0.0064, as determined by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.
(E) Representative bioluminescence images of tumor-bearing SCID mice treated with MeV.