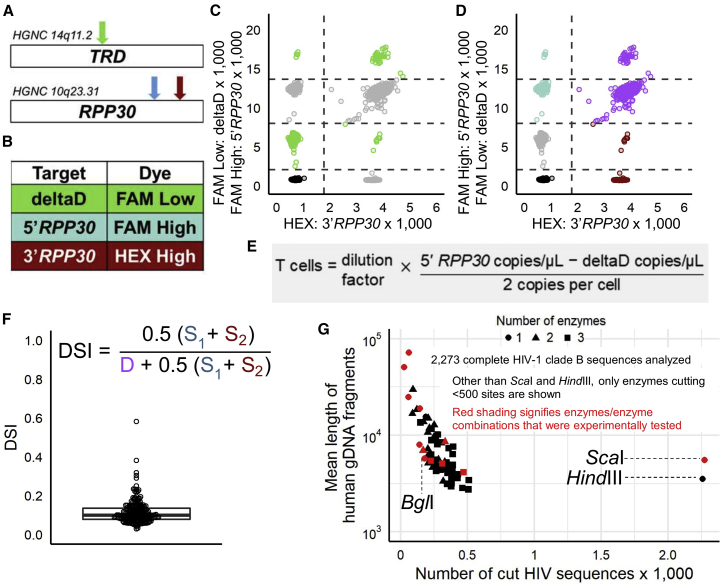
Figure 2.
ddPCR reference assay
(A) Target locations for the ddPCR reference assay within the human genome. The D region target in the T cell receptor gene (TRD) (green arrow) is located on chromosome 14 and is lost during T cell receptor rearrangement (“deltaD”). Thus, the assay directly quantitates all non-T cells. The two RPP30 targets are located ~11 kbp apart from each other within the RPP30 gene on chromosome 10 (blue and red arrows).
(B) Probe targets and corresponding dyes.
(C) Representative PBMC sample indicating droplets positive for the deltaD target (green dots), used to estimate non-T cell numbers.
(D) Same plot as (C) but indicating droplets positive for only the 5′RPP30 (blue dots), only the 3′RPP30 target (red dots), or both RPP30 targets (purple dots). The RPP30 targets are analyzed independently from the deltaD target to quantify shearing and total cells.
(E) Formula used to calculate the number of total T cells. Division by 2 is necessary because each cell contains two gene copies. Dilution factor signifies dilution of the test sample for cell counting relative to the template for the HIV-1 ddPCR assay, which is undiluted.
(F) DSI distribution for 225 PBMC-derived CD4+ T cell samples. The formula for the DNA Shearing Index (DSI), the DSI-corrected number of triple-positive proviral copies, is given, where D represents the count of droplets positive for both RPP30 targets (i.e., double positive) and S1 and S2 represent counts of droplets that are single positive for the 5′RPP30 and 3′RPP30 targets, respectively.
(G) In silico analysis of the number of cutting sites in the HIV genome and mean human gDNA fragment length resulting from digestion by individual or combinations of commonly available restriction enzymes. The red symbols indicate those enzymes we subsequently tested in vitro. Two to four replicate wells were run for each test. ScaI and HindIII are typically recommended for digestion of gDNA prior to ddPCR. BglI yielded the best compromise between cutting very few HIV-1 sequences in the LANL HIV sequence database and cutting the human genome into ideal fragments for droplet generation, averaging ~6 kbp.