Figure 1.
p53 signaling is hyperactivated in cells from XLID patients with mutated HUWE1
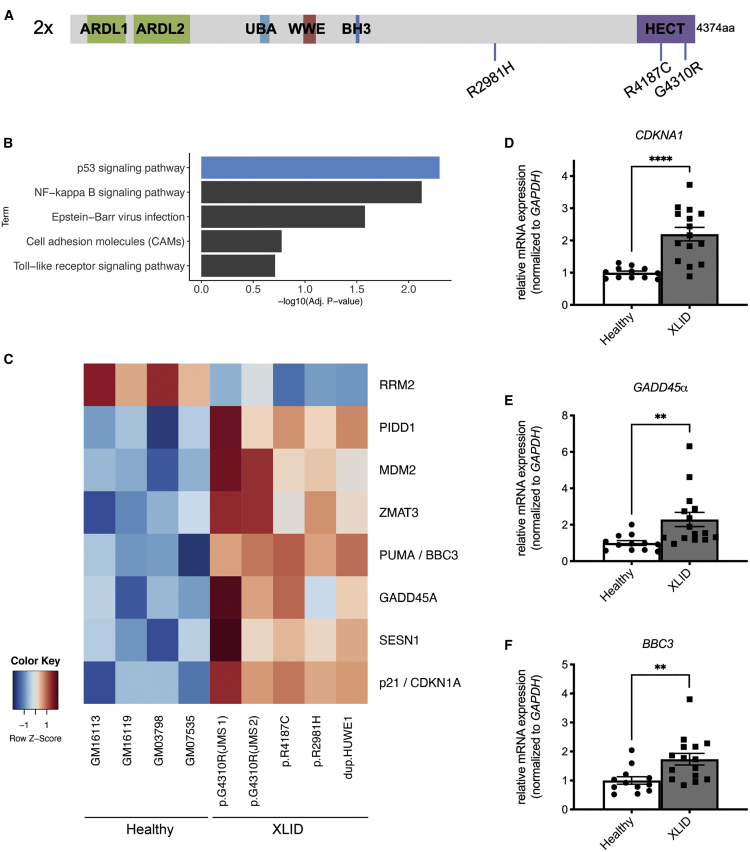
(A) Schematic representation of XLID-causative HUWE1 mutations analyzed in this study (p.R2981H, p.R4187C, and JMS-p.G4310R; HUWE1 duplication: 2×). Depicted HUWE1 domains: ARLD1/2, Armadillo repeat-like domains 1/2; UBA, ubiquitin-association domain; WWE, tryptophan-tryptophan-glutamate domain; BH3, Bcl-2 homology 3 domain; HECT, homologous to E6-AP carboxyl terminus domain.
(B) Top five most significant KEGG pathway terms as determined by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of common differentially expressed genes in XLID patient-derived lymphoblastoid cells (LCs) compared with healthy individual cells (Benjamini corrected p < 0.05).
(C) Heatmap of common differentially expressed genes in XLID compared with healthy LCs belonging to the KEGG p53 signaling term.
(D–F) mRNA levels of p53 target genes CDKN1A/p21 (D), GADD45α (E), and BBC3/PUMA (F) determined by qRT-PCR analysis of four healthy (GM03798, GM07535, GM16113, and GM16119) and five XLID LCs with mutated HUWE1 (p.R2981H, p.R4187C, JMS-p.G4310R, and HUWE1 duplication).
All error bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 3, biological replicates). Two-tailed unpaired t test; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001.