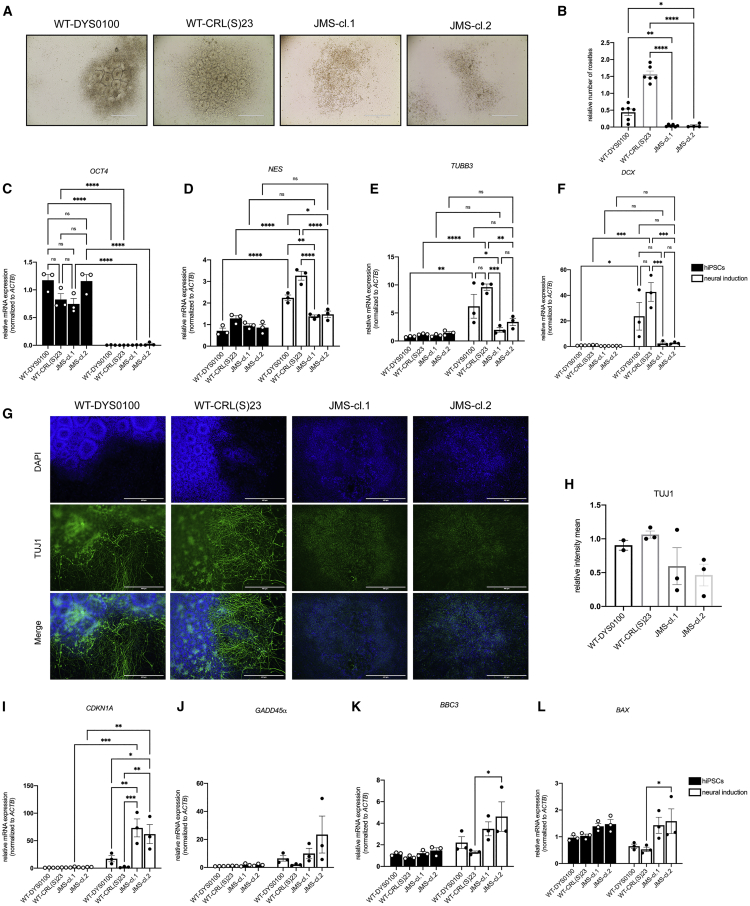
Figure 3.
Neural differentiation of JMS patient hiPSCs is impaired and accompanied by activation of p53 signaling
(A) Representative bright-field images of neural differentiation of healthy control hiPSCs (WT-DYS0100 and WT-CRL(S)23) and two hiPSC clones from a JMS patient expressing HUWE1 p.G4310R (JMS-cl.1 and JMS-cl.2) at day 11; neural rosette structures are visible.
(B) Relative number of rosettes formed in WT and JMS clones (n ≥ 3, biological replicates).
(C–F) qRT-PCR analysis of gene expression of OCT4 (C), NES/NESTIN (D), TUBB3/TUJ1 (E), and DCX (F) in WT and JMS hiPSCs and neural cells (collected at day 13) (n = 3, biological replicates).
(G) Immunofluorescence analysis of TUJ1 in WT and JMS hiPSCs at day 13 of neural differentiation.
(H) Relative intensity of the TUJ1 signal in WT and JMS clones from experiments like the one in (G) (n ≥ 2, biological replicates).
(I–L) qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of the p53 target genes CDKN1A/p21 (I), GADD45α (J), BBC3/PUMA (K), and BAX (L) in WT and JMS hiPSCs and neural cells (collected at day 13) (n = 3, biological replicates).
All error bars indicate mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-test (B); two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-test (C–F and I–L); ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001, n.s. ≥ 0.05. Scale bar: 400 μm. See also Figures S2 and S3.