Fig. 1—
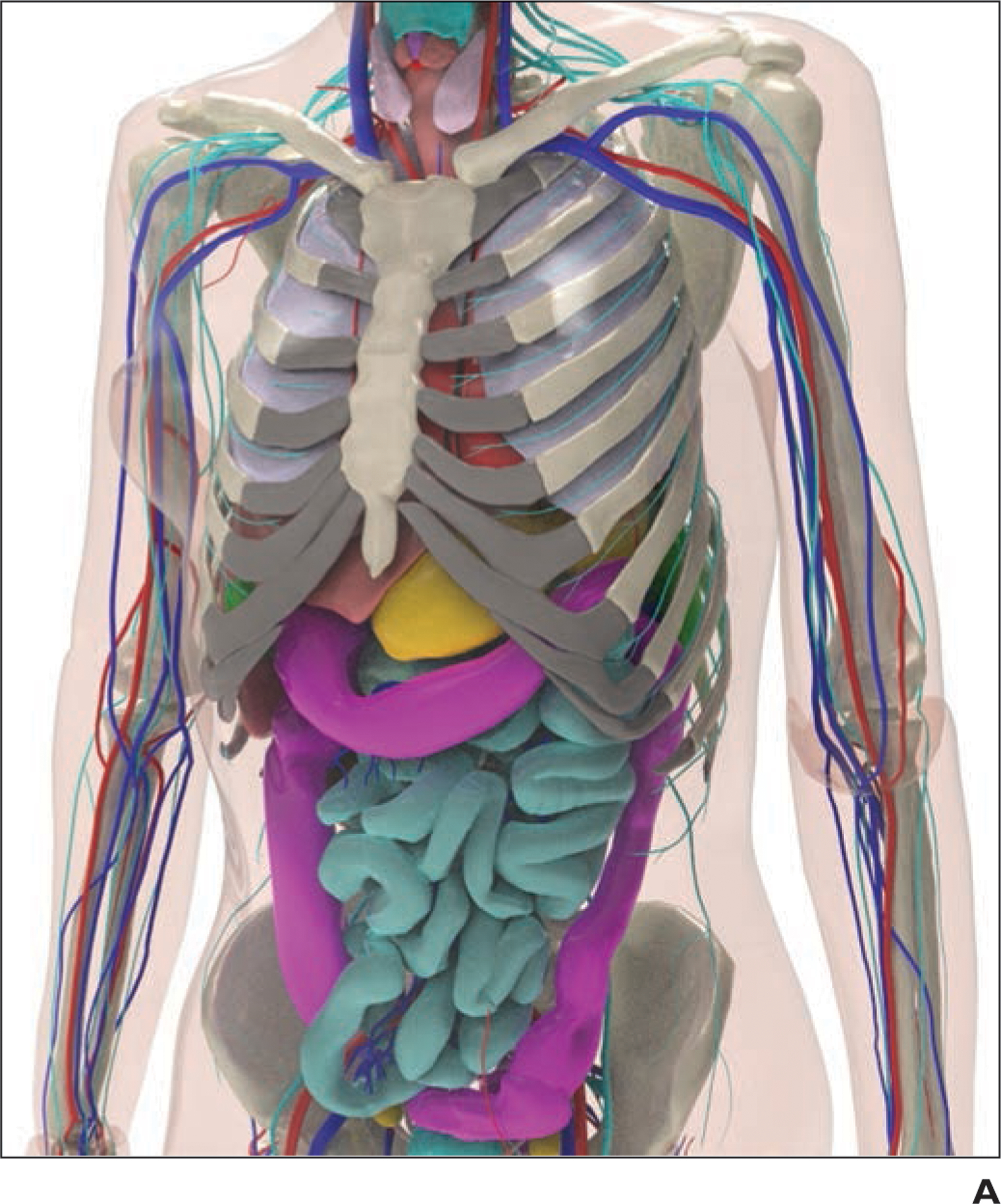
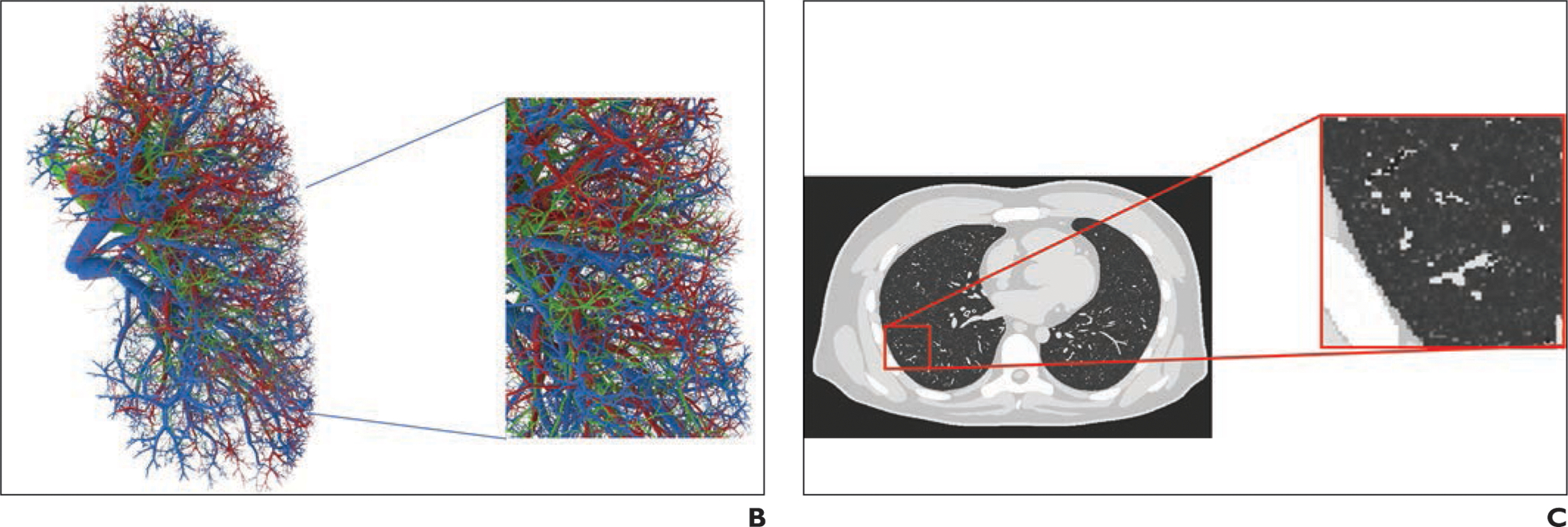
Example of 4D extended cardiac-torso (XCAT) phantom developed at Duke University.
A, Representative computational model shows female XCAT phantom with anthropomorphic organs and structures.
B, Representative computational model shows lung stroma intraorgan structure of XCAT phantom that was developed using anatomically informed mathematic model. Inset shows enlarged view for better visibility of details and small structures.
C, Voxelized rendition (ground truth) of XCAT phantom highlights detailed model of lung parenchyma. Inset shows enlarged view for better visibility of details and small structures.
