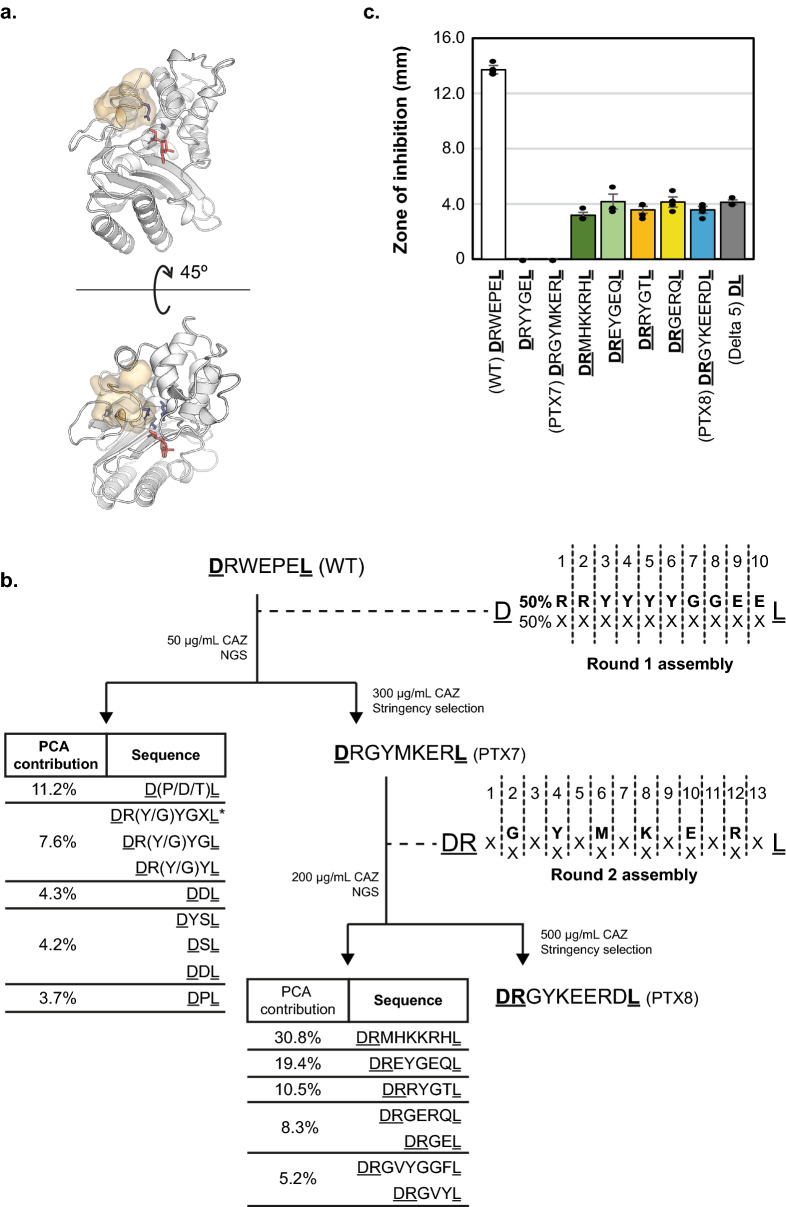
Figure 2.
Directed evolution of TEM-1 Ω-loop variants with altered substrate specificity. (a) TEM-1 beta-lactamase in complex to substrate analogue inhibitor (PDB: 1TEM) as generated by PyMOL39. Inhibitor is shown in the TEM-1 active site in black, and side chains of key catalytic residues (S70, K73 and E166) are shown. The Ω-loop is shown in grey and superimposed to its translucent space-filling representation. (b) Summary of the directed evolution of TEM-1. A 1st round library, biased towards the generation of RYYGE variant was assembled (each cycle containing 50% of a specific building block and 50% of a mixture of the remaining 19 blocks) and selected. Next generation sequencing (NGS) confirms RYYGE was significantly enriched (DRYYGEL was the 16th most frequent sequence post-selection and picked up in the 2nd PCA dimension—see Supplementary Table 1). PTX7, isolated from a high-stringency selection, was used as seed for the 2nd round library. Assembly of the second-round library interspersed cycles of random insertion (all possible blocks in equimolar concentrations) and the same 50%/50% approach used in round 1. PTX8 and sequences from the top four PCA (Principal component analysis) dimensions were further characterized. (c) Ceftazidime resistance of selected variants, measured by inhibition of growth around antibiotic-soaked paper discs—higher values indicate lower resistance (n = 3, error bars represent S.E.M). Underlined residues represent the invariant edges of the assembly, constant in each library and required for library amplification.