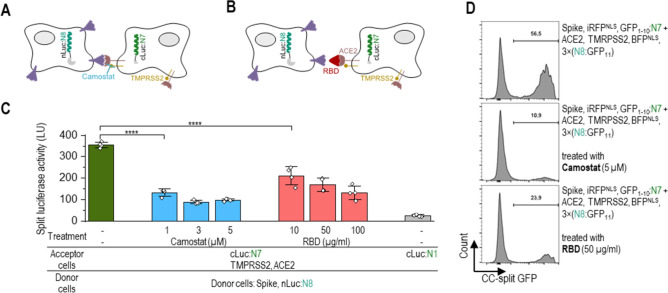
Figure 6.
Detection of inhibition targeting different steps in Spike-protein-hACE2-mediated fusion determined by the CC-reporter assay. (A, B) Schematic representation of inhibition of SARS CoV-2 S protein-mediated cell–cell fusion by TMPRSS2 protease inhibitor Camostat (A) and soluble RBD protein domain binding to the ACE2 receptor (B). (C) Luciferase activity of a mixture of donor and receptor cells treated with Camostat or RBD. Donor cells were transfected with plasmids expressing nLuc:N8 (1000 ng), CoV-2 S protein (10 ng), and the acceptor cells expressed cLuc:N7 or cLuc:N1 as control (1000 ng), ACE2 (20 ng), TMPRSS2 (30 ng). The donor and acceptor cells were mixed and treated with RBD or Camostat. Luciferase activity was measured 3 h later. The values represent the means (± s.d.) from four independent cell cultures, individually transfected with the same mixture of plasmids, and are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of a mixture of donor cells expressing the SARS CoV-2 S protein (50 ng), iRFPNLS (50 ng), and GFP1-10:N7 or GFP1-10:P7 (500 ng) and the acceptor cells expressing ACE2 receptor (250 ng), TMPRSS2 (50 ng), BFPNLS (50 ng), and N8:GFP11, P8:GFP11 or 3 × (N8:GFP11) (650 ng). Percent of reconstituted split GFP for double iRFP and BFP positive population 3 h after mixing donor and acceptor cells treated with Camostat or RBD. For gating strategy, see Fig S8B. Representative results of two independent experiments are shown. For amounts of plasmids, see Table S2. Statistical analyses and the corresponding p-values are listed in Table S3.