Fig. 2. Mechanisms of action of PARP inhibitors in HR-proficient or HR-deficient cancers.
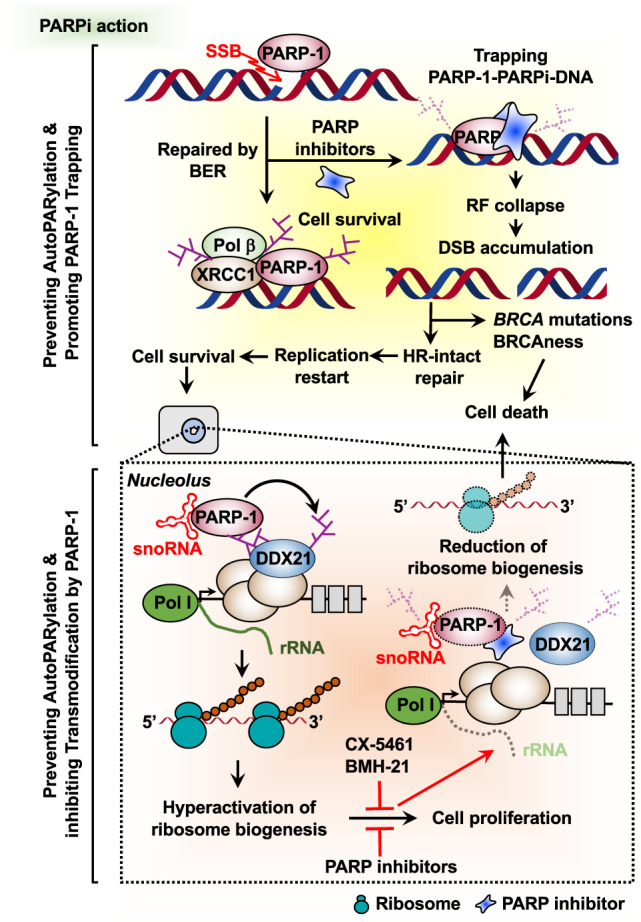
PARP-1 activation upon DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs) catalyzes PARylation, which is required for the accumulation and stabilization of base excision repair (BER) components. PARPi selectively induces synthetic lethality by blocking the repair of damaged DNA in the context of cells with homologous recombination (HR) deficiency (upper panel). Alternatively, PARPi reduce hyperactivated ribosome biogenesis by snoRNA-activated PARP-1, regardless of HR-mediated DNA repair deficiency (lower panel).
