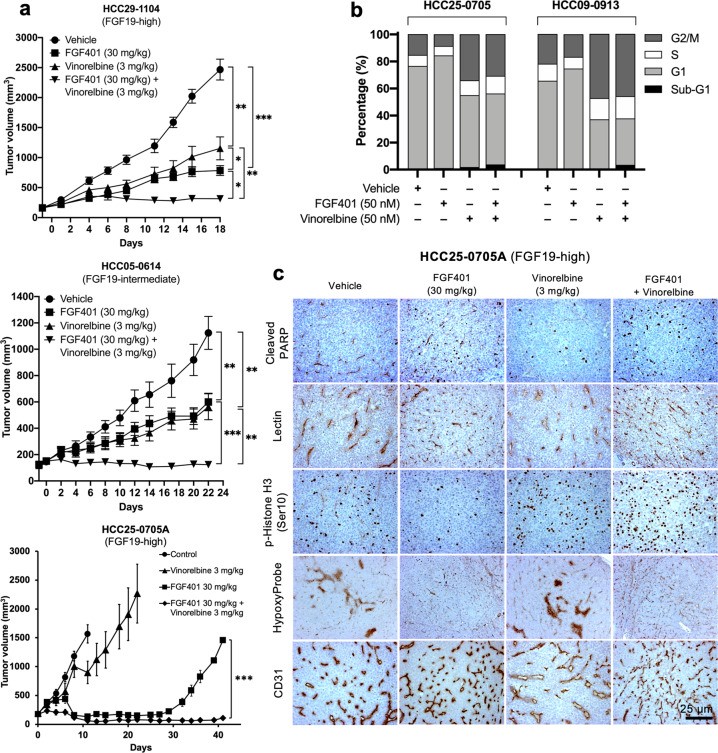
Fig. 5. Effects of FGF401, vinorelbine and FGF401 plus vinorelbine on tumor growth, cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, tumor hypoxia, and blood vessel normalization in high FGF19-expressing HCC models.
Tumors were implanted subcutaneously, and mice were randomized into groups and treated with 200 µl of vehicle, 30 mg/kg FGF401 twice daily, 3 mg/kg vinorelbine once every 3.5 days or the combination of FGF401 plus vinorelbine. The mean tumor volumes ± SEs are plotted (a). Primary cultures from HCC25-0705A and HCC09-0913 tumors were treated with vehicle, FGF401 or vinorelbine for 24 h and subjected to cell cycle analysis (b). HCC25-0705A tumors were stained for cleaved PARP, lectin, p-Histone H3 Ser10, hypoxia (Hypoxyprobe), and CD31 (blood vessels) (c). *p < 0.01; **p < 0.001.