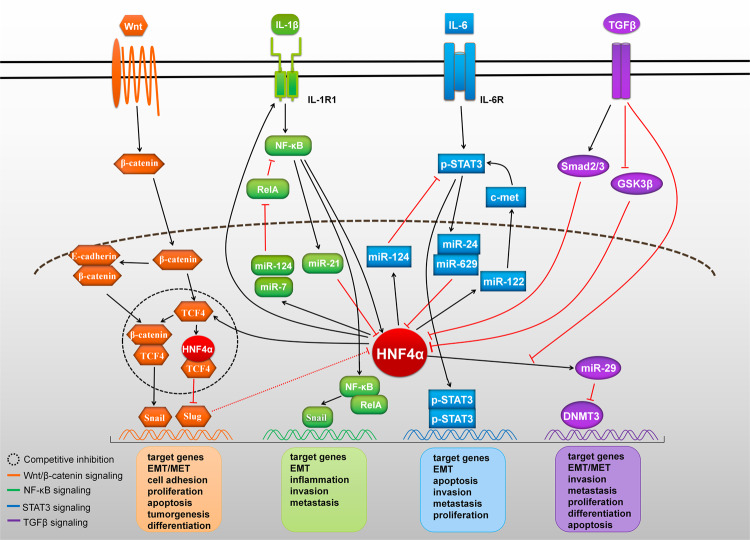
Fig. 2. Role of aberrant HNF4α-related cell signaling pathways in cancer.
HNF4α in cancer cells mainly acts through the Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB, STAT3, and TGFβ signaling pathways to increase cell migration and invasion and decrease apoptosis. High expression of HNF4α regulates target genes by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin, STAT3 and TGFβ signaling pathways. After induction by stimuli, high HNF4α expression can activate the NF-κB signaling pathway to promote tumor progression or inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway to downregulate target genes. Aberrant HNF4α-related Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB, STAT3 and TGFβ signaling pathway activity is involved throughout the EMT process.