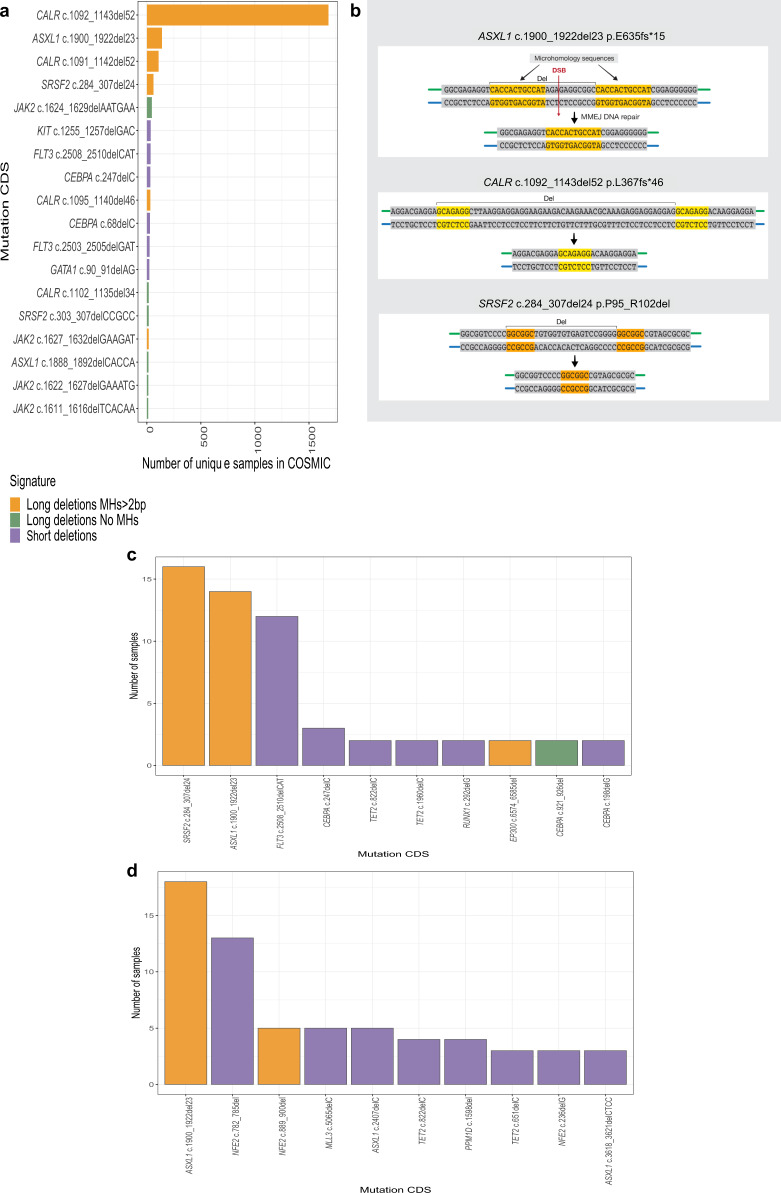
Fig. 1. Most common deletions in myeloid malignancies share an MH-based signature.
a Number of samples carrying somatic deletion (represented by gene and mutation CDS (coding DNA sequence) names) in myeloid malignancies from COSMIC dataset. Deletions that were identified in 10 or more unique samples are shown. Deletion signatures are: long (≥5-bp) deletions with flanking microhomologies (MHs) of at least 2 bp (orange), long (≥5-bp) deletions with flanking MHs of zero or 1 bp (green) and short deletions (<5-bp) (purple). A single base mismatch was allowed. b MH-based deletion signature in ASXL1, CALR and SRSF2 genes. Upon double-strand break (DSB) (red arrow) at genomic loci located between two MH sequences (orange and yellow), DNA repair (vertical black arrow) involves a deletion (Del) of one MH and the sequence between the two MHs. c, d Number of samples carrying the 10 most common somatic deletions (represented by gene and mutation CDS (coding DNA sequence) names) in 1540 adult acute myeloid leukemia (c) and 2045 Myeloproliferative neoplasm (d) datasets. Deletion signatures are as described in a. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.