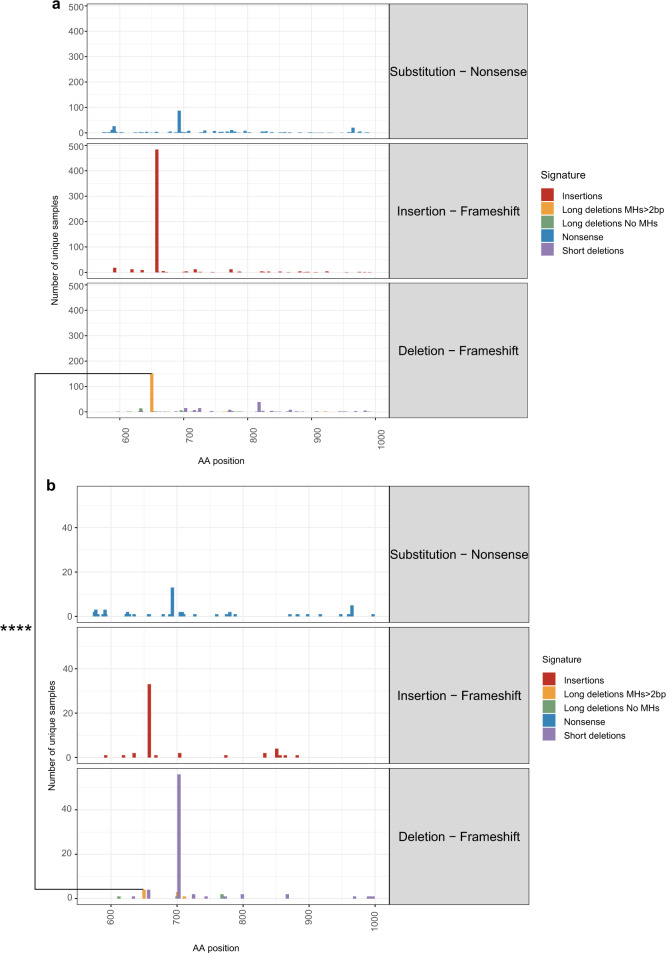
Fig. 2. High recurrence rates of ASXL1 MH-based deletion in myeloid malignancies are driven by specific mutational mechanisms.
a, b Number of samples carrying somatic truncating mutations in ASXL1 gene and the position of the last amino acid of ASXL1 protein (AA position) as identified across n = 1434 hematologic (a) and n = 252 non-hematologic (b) tumors in COSMIC dataset. Deletions signatures are Nonsense substitutions (blue), frameshift insertions (red), frameshift ≥5-bp deletions with flanking microhomologies (MHs) of at least 2 bp (orange), frameshift ≥5-bp deletions with flanking MHs of zero or 1 bp (green) and frameshift short deletions (<5-bp) (purple). The proportions of MH-based deletion cases (orange) out of the total deletion cases (purple, green and orange) were compared between hematologic (153/376) and non-hematologic (4/103) tumors. Chi squared test with yates correction for continuity was used to determine statistical significance. (****p = 4.136e-12). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.