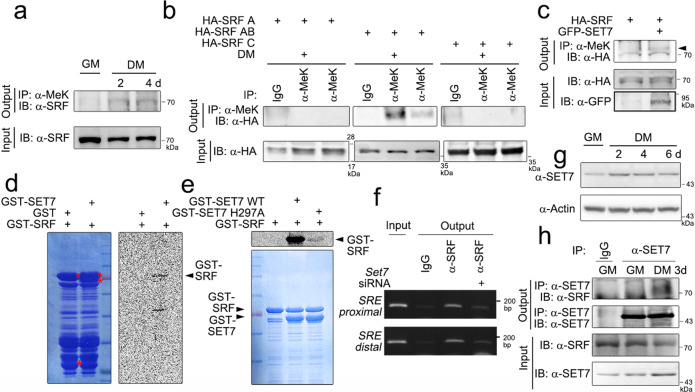
Fig. 4. Myoblast differentiation induces SET7-dependent methylation of the SRF MADS-box.
a Immunoprecipitation-based in vivo cellular methylation assay using anti-methylated lysine (anti-α-MeK) antibody revealed that SRF was methylated during C2C12 differentiation. Notably, methylation was increased in the cells cultured in differentiation medium (DM). b HA-tagged truncated mutants of SRF (SRF-A, SRF-AB, and SRF-C) were transfected into C2C12 cells, and then, the cells were subjected to serum deprivation (DM). The SRF MADS-box region was methylated, as determined with a α-MeK immunoprecipitation-based assay. c Transfection of SET7 induced the methylation of SRF in the C2C12 cells. d In vitro methyltransferase assay in complete cell-free conditions showing that the chimeric protein GST-SET7 induced the methylation of GST-SRF. GST protein served as a control. Left: Coomassie blue staining was used to determine the expression of GST proteins. Right: Autoradiograph. e Enzymatically dead SET7 (SET7 H297A) failed to induce the methylation of SRF. f Set7 siRNA attenuated the binding of SRF to the proximal SRE in the Acta1 gene promoter. ChIP analysis. g Expression of SET7 was increased during C2C12 differentiation. h Association between endogenous SET7 and SRF was enhanced in DM.