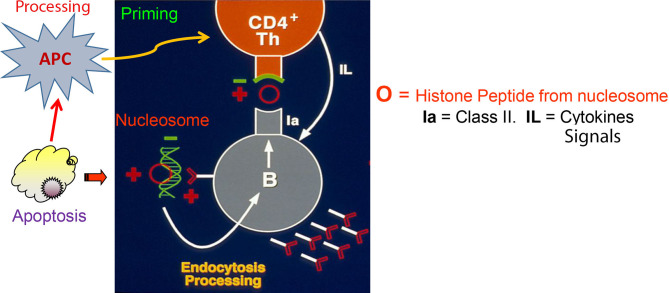
Figure 1.
Autoimmune T and B cell interaction in lupus based on Nucleosome-derived autoantigens (based on work done from early 1980s through early1990s; references in the Text). Figure shows that Th cells that induce the production of pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies possess anionic residues in CDR3 of their TCRs (green). The lupus Th cells recognize peptides with reciprocal cationic charge (red), such as peptides from histones in nucleosomes presented by the pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibody producing B cells bearing BCRs with cationic residues generated by somatic mutations in CDR3 of their receptors (red). The pathogenic BCRs bind to anionic residues in DNA (green) that are complexed with cationic histones in nucleosomes, which are then endocytosed and processed for presentation to the interacting Th cells. Nucleosomes accumulate due to defective clearance of apoptotic cells in lupus, and are processed by activated APC to prime the pathogenic Th cells; a lupus-specific event initiated early in life. This figure is extensively modified from a figure in J Exp Med (60).