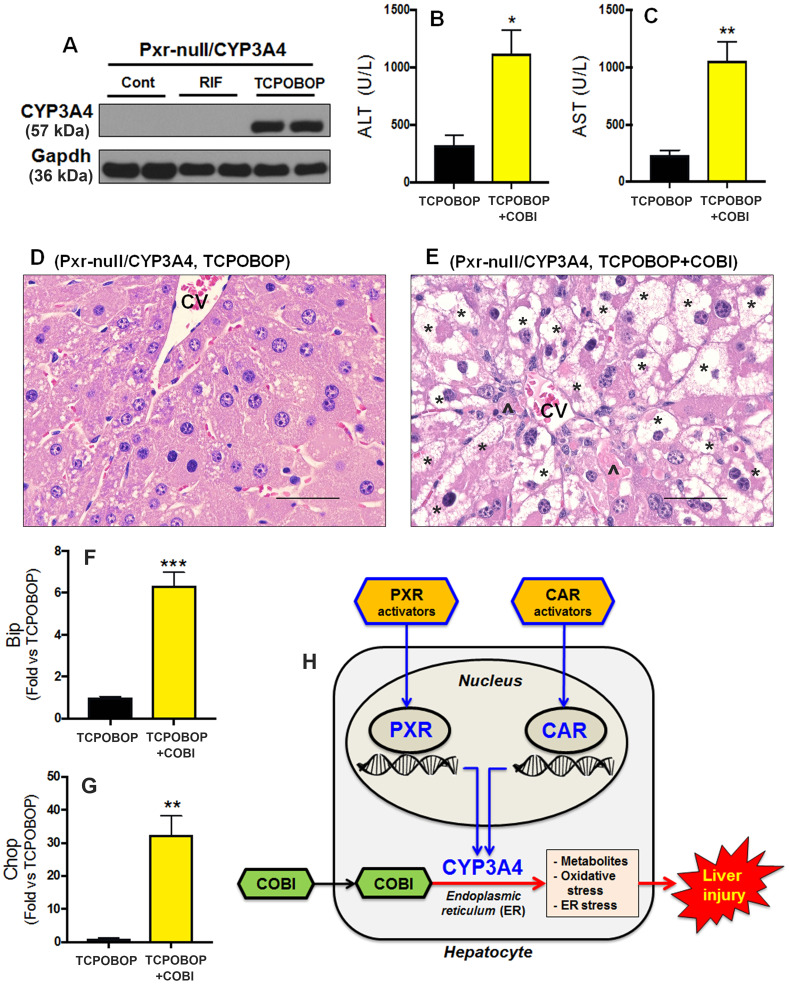
Figure 5.
Roles of xenobiotic nuclear receptors PXR and CAR in COBI hepatotoxicity. A, CYP3A4 expression in the liver of Pxr-null/CYP3A4 mice pretreated with RIF (PXR activator) or TCPOBOP (CAR activator). CYP3A4 was analyzed by Western blotting. Gapdh was used as a loading control. B, C, Serum activities of ALT and AST in Pxr-null/CYP3A4 mice pretreated with TCPOBOP followed by COBI. D, E, Histological analysis of liver samples from Pxr-null/CYP3A4 mice treated with TCPOBOP and TCPOBOP+COBI. Hepatocyte degeneration (*) and cell death (^) were observed in TCPOBOP+COBI group (E). CV, central vein. Scale bars: 50 µm. F, G, The expression of genes related to ER stress in the liver of Pxr-null/CYP3A4 mice pretreated with TCPOBOP followed by COBI. mRNAs of Bip (F) and Chop (G) were analyzed by qPCR. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–7). Statistical significance was determined by the two-tailed Student’s t test. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001. H, A scheme showing the roles of PXR and CAR in COBI hepatotoxicity. Activation of PXR and CAR leads to CYP3A4 induction in hepatocytes. Overexpressed CYP3A4 in the ER increases the metabolism and bioactivation of COBI to form reactive metabolites, which can directly target the ER leading to oxidative stress, ER stress, and hepatocellular injury.