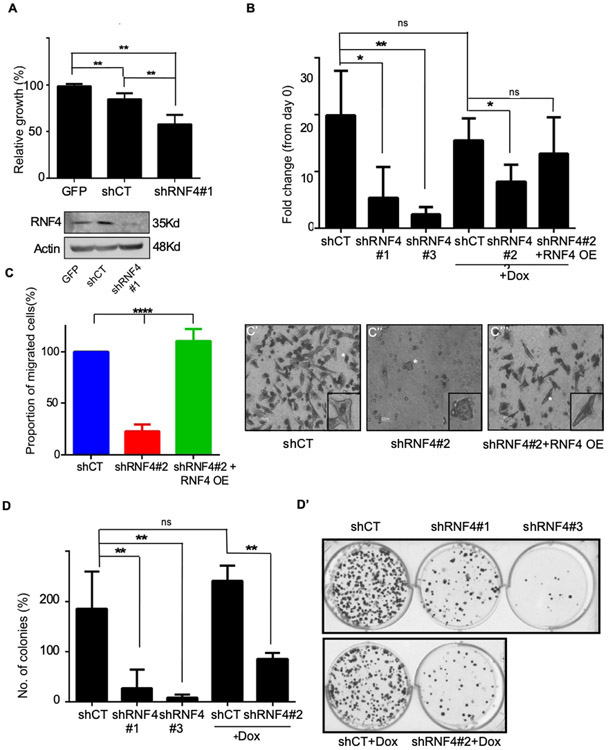
Figure 2: RNF4 is essential for proliferation, migration, and clonogenicity of human melanoma cells.
(A) Upper panel: Mitochondrial activity of A375 melanoma cells as determined by MTT assay. Cells were infected with GFP or the indicated lentiviral shRNA vectors, **=p<0.01; n=3. Lower panel: Western blot analysis of cells used in A. Actin serves as loading control. (B) Viability of A375 cells as determined by ATP-lite® assay **=p<0.01; *=p<0.05; ns: non-significant; n=3. (C-C’”) Trans-well migration assay of A375 human melanoma cells infected with the indicated vectors. Quantification is shown in (C), and (C’-C’”) are representative images. White stars indicate cells shown in the insets. Where indicated in (B), and in (C), the activation of shRNF4#2 and RNF4 over-expression (RNF4 OE) are induced by the addition of Dox. The RNF4 OE vector is not sensitive to the shRNF4#2. (D-D’) Colony formation assay of A375 cells. Cells were infected with the indicated shRNA vectors. (D) Quantification of three biological repeats **= P<0.01; n=3 (D’) representative wells. shCT denoted scrambled RNF4 control; shRNF4#1-3 are shRNAs targeting RNF4.