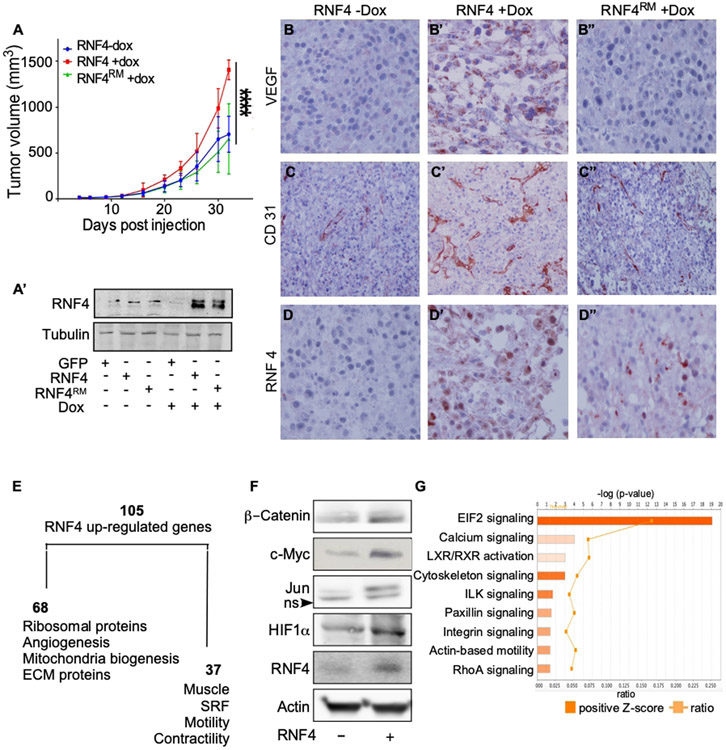
Figure 3: RNF4 potentiates the growth of melanoma cells after xenografting in immunodeficient mice.
(A) Tumor size of A375-expressing Dox-inducible RNF4 or RNF4C159A catalytic inactive RING mutant (RNF4RM) injected subcutaneously to xenograft nude mice in the absence or presence of Dox, as indicated (−/+Dox; n=7 per group; ****=p<0.0001). (A’) Western blot analysis of RNF4 protein level in transplanted A375 cells at time of transplantation. (B-D”) Representative immuno-histochemistry images with indicated antibodies (immunoperoxidase, x200). Dox-induced the expression of RNF4 (B’-D’) or RNF4RM (B”-D”) in indicated tumors. (E) A diagram of RNF4-upregulated genes identified by RNA-seq of RNF4-expressing tumors and respective gene ontology. (F) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in A375 cells expressing GFP control or RNF4. (G) Ingenuity upstream pathway analysis (IPA) of RNF4-expressing tumors. Positive-z scores indicated in orange.