Fig. 1. Plant homologs of Dhh1/DDX6 are novel components of D-bodies.
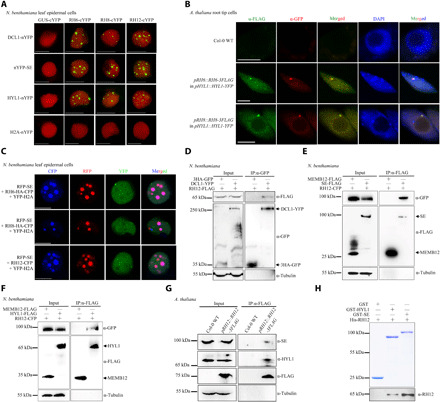
(A) BiFC analyses of N. benthamiana cells coexpressed with NLS-mCherry. YFP signals (green) and mCherry fluorescent signals (red) were observed at 72 hours post-inoculation (hpi). Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence analyses performed in A. thaliana root tip cells in the elongation region of stable transgenic plants. The immunofluorescence of RH6-3FLAG/RH8-3FLAG appears green, and the immunofluorescence of HYL1-YFP appears red. The positive cell percentages in the RH6-3FLAG and RH8-3FLAG lines were 74% (n = 87) and 80% (n = 70), respectively. The blue signals from 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) represent nuclei. Scale bars, 5 μm. (C) Colocalization of RFP-SE together with RNA helicases in N. benthamiana. Fluorescence was analyzed at 72 hpi. Scale bars, 5 μm. YFP-H2A was used as nuclear marker. (D to F) Co-IP assays in N. benthamiana showing interactions between RH12 and DCL1 (D), SE (E), or HYL1 (F). (G) Co-IP assays in pRH12::RH12-3FLAG transgenic A. thaliana plants showing interactions between RH12 with SE and HYL1. (H) Detection of the direct interactions between RH12 with SE and HYL1 by pull-down assays. GST, GST-HYL1, and GST-SE (top) were used as matrix-bound bait, where RH12 served as prey. WT, wild type.
