FIG 5. Inhibiting ceramide production decreases ROS and apoptosis induced by HDM.
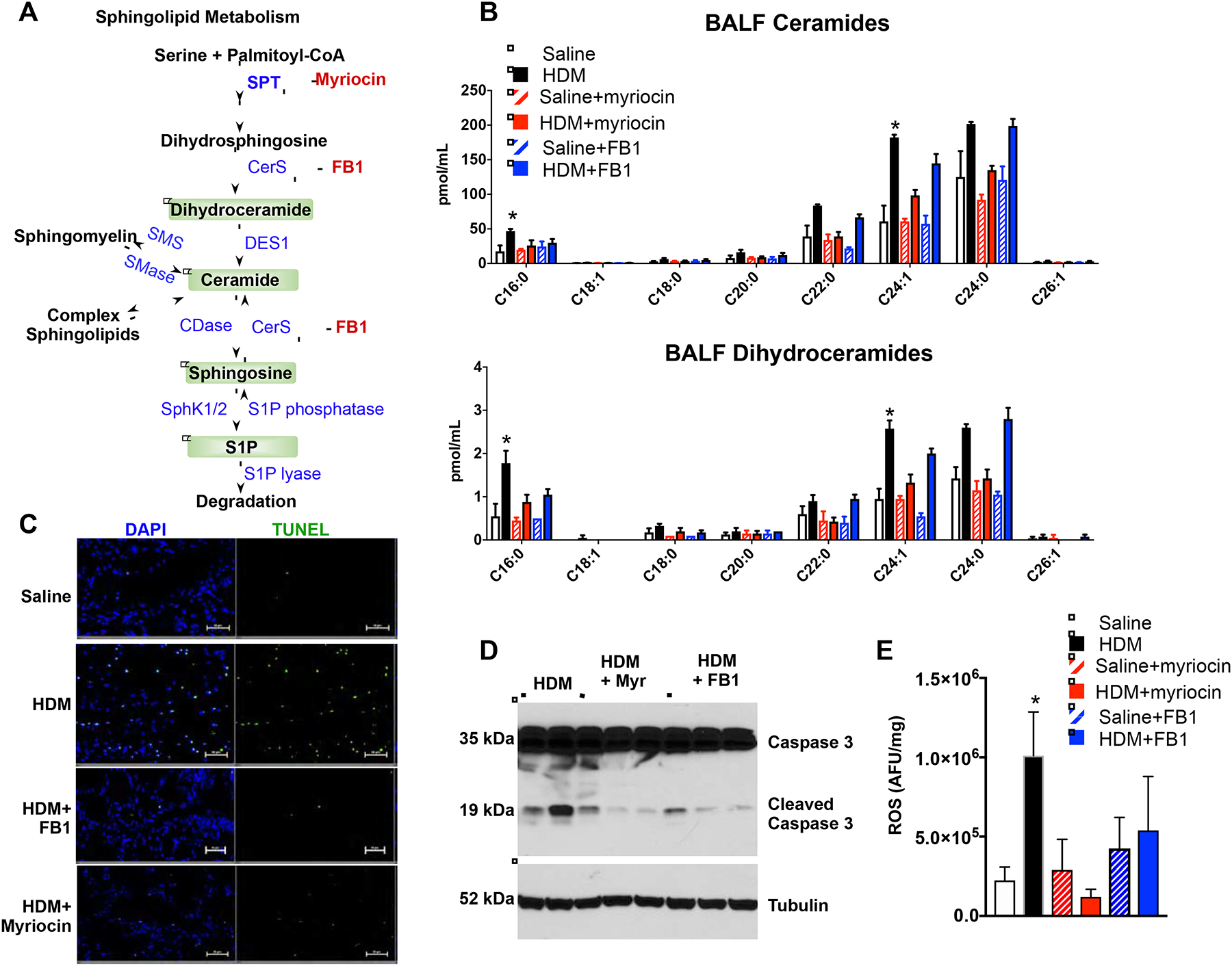
(A–C) Mice were challenged daily intranasally with HDM or saline for 5 consecutive days from days 1 to 5 and from days 8 to 12. Mice were injected i.p. with vehicle, myriocin (Myr; 0.3 mg/kg), or fumonisin B1 (FB1, 0.5 mg/kg) 30 min prior to the HDM challenges on days 10, 11, and 12 and lungs were examined on day 15. (A) Scheme of ceramide formation by de novo biosynthesis and degradation. Myriocin inhibits SPT and FB1 inhibits ceramide synthases (CerS). (B) Sphingolipids were extracted from BALF and ceramide and dihydroceramide species measured by LC-ESI-MS/MS. (C) In situ TUNEL staining of lung sections. Size bars: 50 μm. (D) Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase 3 in the lung. (E) ROS was measured fluorometrically. Data are mean ± SD. B: n=4 for saline, 4 for HDM, 2 for saline+myriocin, 4 for HDM+myriocin; 2 for saline+FB1, 4 for HDM+FB1; D: n= 2,3 and 3 respectively; E: n=3 for saline, 7 for HDM, 2 for saline+myriocin, 3 for HDM+myriocin; 2 for saline+FB1, 4 for HDM+FB1. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to each saline control.
