FIG 6. Association between asthma severity and ceramide species that are increased in BALF.
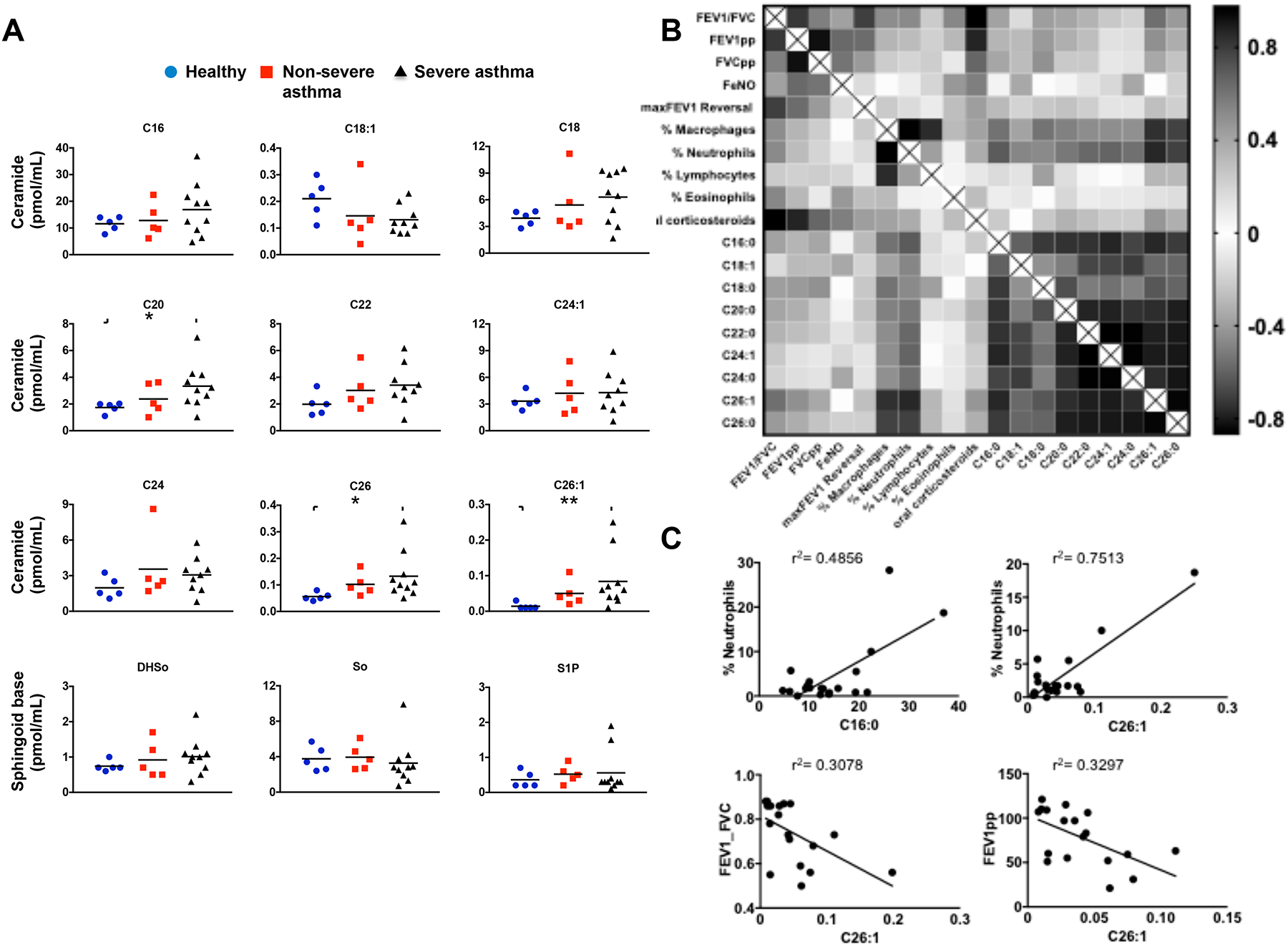
(A) Levels of ceramide species in BALF from healthy controls, non-severe asthmatics, and severe asthmatics described in Table I were measured by LC-ESI-MS/MS. * P < 0.05 compared to healthy controls. (B) Heat-map of matrix coefficient correlation of each ceramide species in the BALF and lung functions or immune cells infiltration. Visualization of the correlations between each pair of variables using product-moment coefficients. Stronger Pearson correlation coefficients (r) are represented by black color. (C) Examples of correlations between C16 or C26:1 ceramides and neutrophils, and lung functions. Goodness of fit is indicated by r2. Correlation of neutrophils with C16-ceramide (Spearman r = 0.3089 and P = 0.092) and with C26:1-ceramide (Spearman r=0.4141 and p = 0.039). Correlation of FEV1_FVC with C26:1-ceramide (Pearson r = 0.5548 and P = 0.01) and FEV1pp with C26:1-ceramide (Pearson r = 0.5742, and P =0.01).
