FIG 7. Increased ceramide in HDM-challenged mice enhances neutrophil recruitment to the lungs.
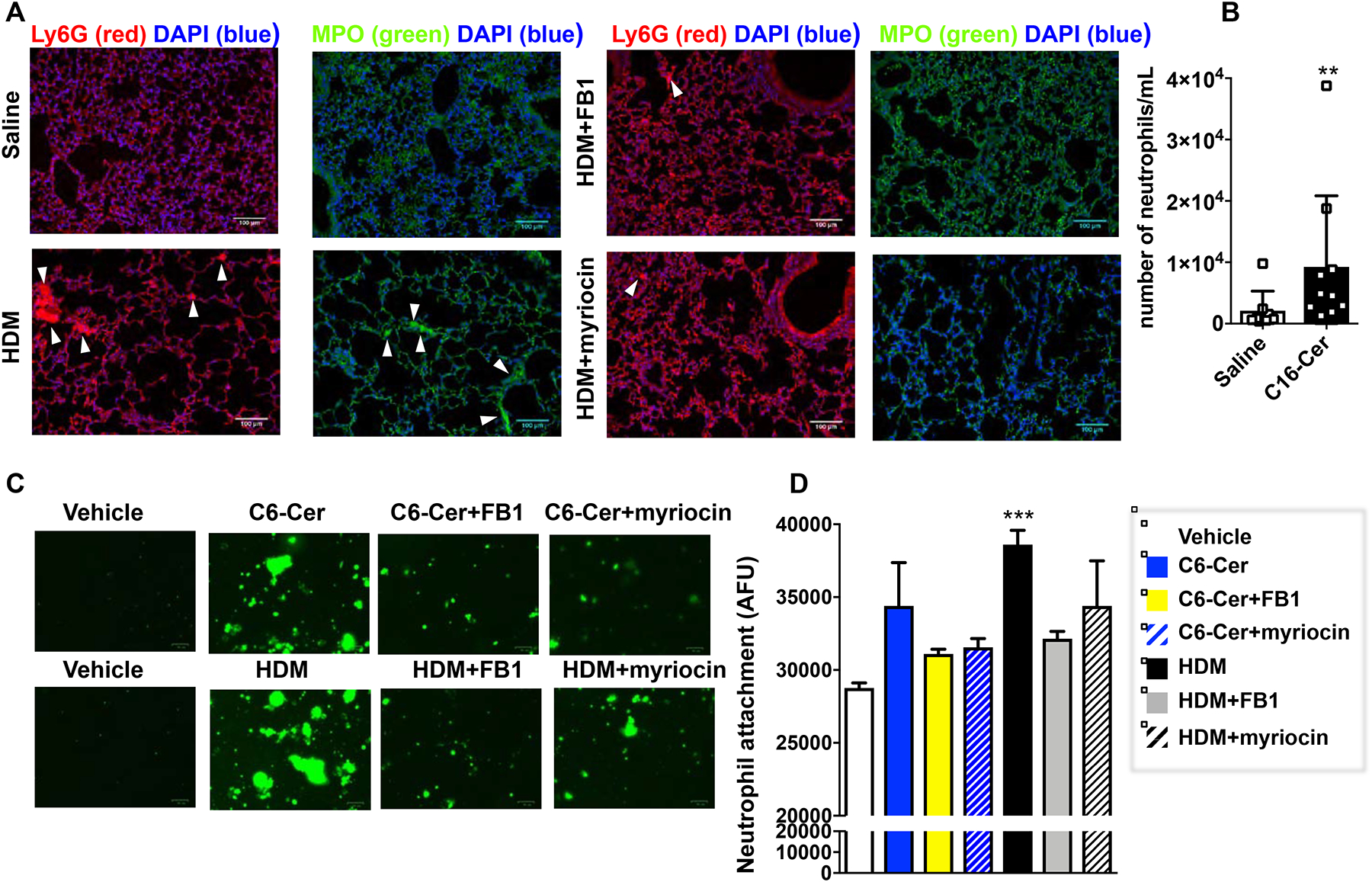
(A) Mice were challenged daily intranasally with HDM or saline for 5 consecutive days from days 1 to 5 and from days 8 to 12. Mice were injected i.p. with vehicle, myriocin (Myr; 0.3 mg/kg), or fumonisin B1 (FB1, 0.5 mg/kg) 30 min prior to the HDM challenges on days 10, 11, and 12 and lungs were examined on day 15 as described in Figure 5. Lung sections were stained with anti-Ly6G (red) or anti-MPO antibody (green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei (blue). Size bar: 100 μm. (B,C) Primary lung epithelial cells incubated for 20 h with vehicle, D-erythro-C6-ceramide (C6-Cer, 1 μM), or HDM (100 μg/mL) in absence or presence of FB1 (1 μM) or myriocin (100 nM) as indicated. After extensive washing, purified labeled neutrophils were added for 4 h and adhesion assessed by fluorescence. (B) Following intranasal instillation of vehicle or C16:0 ceramide number of neutrophils in the BALF was determined by FACS. Data means ± SD. n = 8 and 10 mice/group, respectively. **P < 0.01. (C) Representative fluorescent images. (D) Data expressed as arbitrary fluorescence units are means ± SEM. n=5 for each group. Each sample represents an individual donor mouse. * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01 compared to vehicle.
