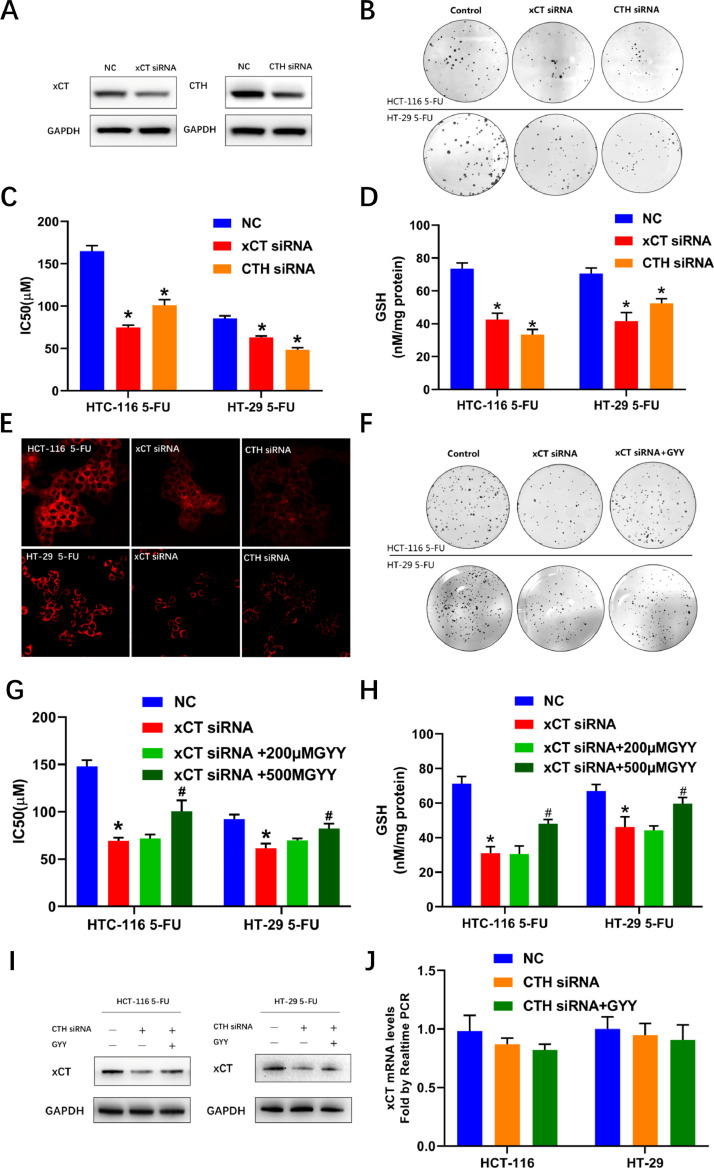
Fig. 2.
CTH-H2S contributes to the 5-FU resistance maintained by xCT overexpression. (A) immunoblots showing inhibiting the expression of xCT or CTH using specific siRNAs. (B) Interfering xCT or CTH expression inhibited clonogenicity of both colon cancer cell lines in the presence of 5-FU. (C) IC50 values of 5-FU after inhibiting xCT and CTH expression in both cell lines. (D) GSH values after inhibiting xCT and CTH expression in both cell lines. (E) H2S fluorescent probe indicating decreased H2S levels in both cell lines after inhibiting xCT or CTH. (F) GYY4137 saved the attenuated clonogenicity in both cell lines after inhibiting xCT. (G) and (H) GYY4137 saved the decreased IC50 of 5-FU and GSH values after inhibiting xCT in both cell lines. (I) GYY4137 promoted the attenuated levels of xCT after inhibiting CTH expression with siRNAs. (J) Quantitative real-time PCR showing no effect of either inhibiting CTH or GYY4137 on xCT mRNA levels. (* P < 0.05 vs negative control [NC], #P < 0.05 vs xCT siRNA groups)