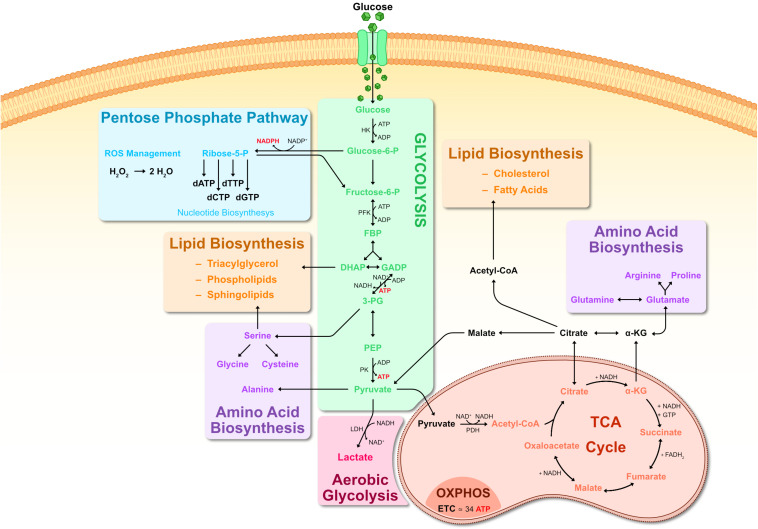
FIGURE 1.
Metabolic pathways of glucose metabolism. Representation of key steps in glucose metabolism. Upon entering the cell, glucose is first metabolized by HK into G6P, consuming ATP. G6P can branch off into the PPP pathway, producing R5P and generating large amounts of NADPH as a byproduct. R5P is a precursor for creating nucleic acids. NADPH generated by the PPP can be used to scavenge ROS via glutathione reduction, converting H2O2 into H2O. G6P is further metabolized into F6P and subsequently into FBP. FBP is metabolized into one molecule of DHAP and another of GADP. DHAP can branch off into lipid biosynthesis where it is a precursor for phospholipids and triacylglycerol. Otherwise, DHAP is transformed into GADP and both GADP molecules are metabolized into 3-PG, generating ATP in the process. 3-PG can be used for serine biosynthesis, which can then contribute toward synthesis of sphingolipids as well as glycine and cysteine. 3-PG goes on to be metabolized into PEP and then into pyruvate by PK activity. Pyruvate can: serve as substrate for alanine biosynthesis; be converted to lactate by LDH (known as anaerobic respiration or aerobic glycolysis); enter a mitochondrion where PDH metabolizes it into Acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA then enters the TCA cycle, where it is metabolized in a series of sequential reactions resulting in citrate, α-KG, succinate, fumarate, malate, oxaloacetate which cycles back to citrate. Some of these reactions generate byproducts such as NADH and FADH2. NADH and FADH2 are then used for OXPHOS, generating ATP in the inner mitochondrial membrane matrix. Abbreviations: α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; 3-PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CoA, coenzyme A; dATP, deoxyadenosine triphosphate; dCTP, deoxycytidine triphosphate; dGTP, deoxyguanosine triphosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; dTTP, deoxythymidine triphosphate; ETC, electron transport chain; F6P, Fructose-6-phosphate; FADH, flavin adenine dinucleotide, reduced; FBP, fructose 1,6-biphosphate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; GADP, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; HK, hexokinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced; NADP, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PK, pyruvate kinase; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.