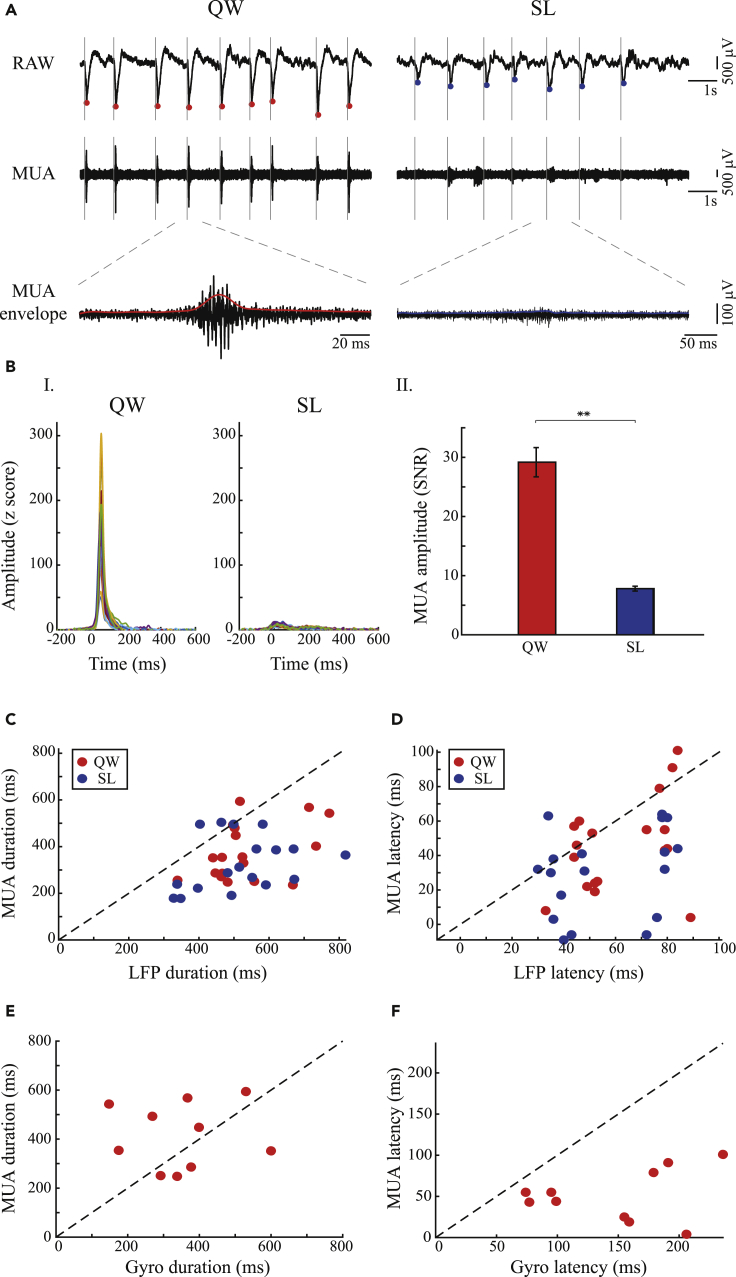
Figure 4.
Focal striatal multiunit activity (MUA) decreases during sleep
(A) LFP spike-related MUA (same session as presented in Figure 1A). Left to right: quiet waking versus sleep. Top to bottom: raw signal, striatal MUA, extension of a single MUA episode (black) and its envelope (colored line). Solid gray line: LFP spike onset, dots: LFP spike peaks (quiet waking, red; sleep, blue).
(B) (I) An example of an MUA envelope, across all electrodes (different colors) in a single session, aligned to LFP spike onset during the quiet waking and sleep states (same session as presented in Figures 1A, 2A, and 4A). (II) The mean SNR of LFP spike-related MUA envelope ±1 SEM, calculated from all electrodes (N = 191) across sessions (N = 18), during the quiet waking and sleep states.∗∗p < 0.001.
(C) Comparison of the duration of the mean LFP spike shapes and the related mean MUA in each session, during the quiet waking state (red) and sleep (blue).
(D) Comparison of the latency of the mean LFP spike shapes and the related mean MUA in each session, during the quiet waking state (red) and sleep (blue).
(E and F) (E) Comparison of the latency of the mean MUA envelope and the related mean tic shape in each session, during the quiet waking state. (F) Comparison of the latency of the mean MUA shape and the related mean tic shape in each session, during the quiet waking state.