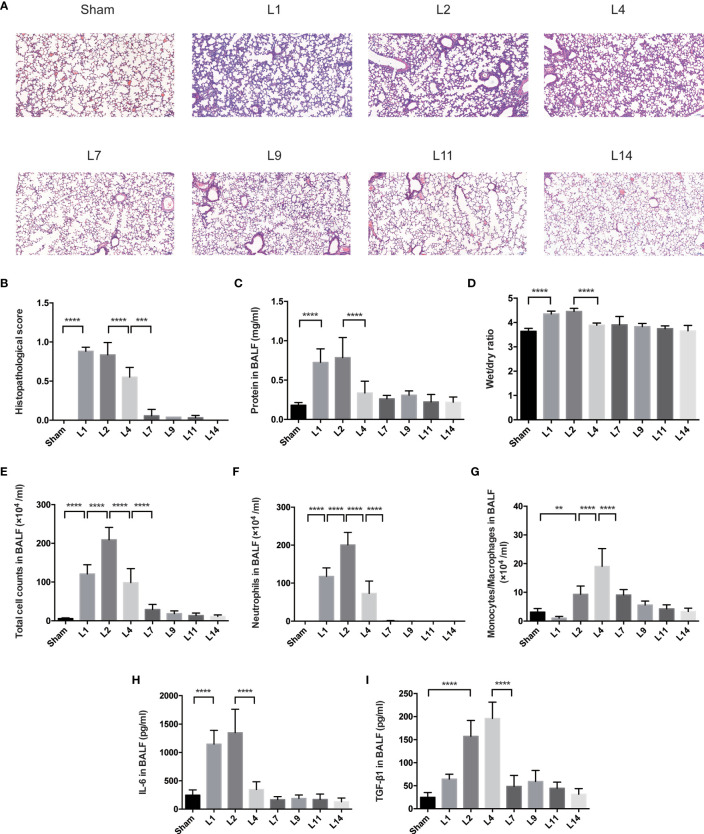
Figure 1.
Lung injury exhibited a dynamic variation within 2 weeks during LPS-induced ARDS. (A) Histopathological staining. Representative HE staining of lung sections are shown 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, 11, 14 days after LPS-induced ARDS. Original magnification = 100×, scale bar represents 100 μm. (B) Histopathological scores of (A). Lung injury was evaluated on a scale of 0–2 for each of the following criteria: i) neutrophils in the alveolar space; ii) neutrophils in the interstitial space; iii) hyaline membranes; iv) proteinaceous debris; v) alveolar septal thickening. The final histopathological scores was as follows: score = [20*(i)+14*(ii)+7*(iii)+7*(iv)+2*(v)]/(number of fields *100) (C) The protein in BALF. (D) The wet/dry ratio of lung tissue. (E) Total cell counts in BALF. (F) Neutrophils in BALF. (G) Monocytes/Macrophages in BALF. (H) Secretion of cytokine IL-6 in BALF. (I) Secretion of cytokine TGF-β1 in BALF. For all panels: mean ± S.D. **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; and ****p ≤ 0.0001 for one-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple t-tests. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. n = 6–8 mice per group.