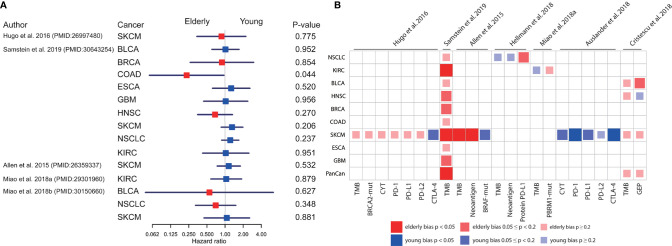
Figure 2.
Comparison of overall survival and molecular profiles in elderly and young patients with ICB treatments. (A) Univariate analyses based on Cox proportional hazards model for elderly and young patients receiving ICB treatment in 9 cancer types from 5 datasets. The squares and horizonal lines represent trial-specific HRs and 95% CIs. Square colors represent OS advantage in elderly (red) and young (blue) patients. (B) The age-bias of molecular biomarkers reported in patients with ICB treatment across multiple cancer types from 7 datasets. Fisher’s exact test for individual gene mutation, and two-sided Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test for other biomarkers. TMB, tumor mutation burden; CYT, cytolytic activity; GEP, T cell-inflamed gene expression profile; BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; COAD, colon adenocarcinoma; ESCA, esophageal carcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma; HNSC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KIRC, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; SKCM, skin cutaneous melanoma; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer.