Figure 1.
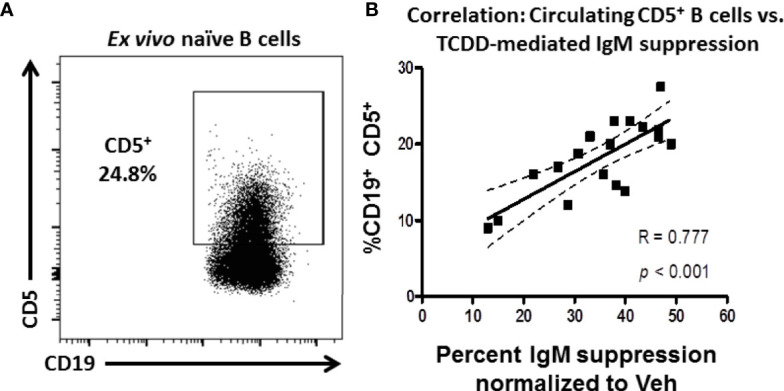
Frequency of CD5 expressing B cells in circulation predicts donor sensitivity to TCDD-mediated IgM suppression. CD19+ naïve human B cells isolated from PBMC by magnetic separation were activated with sCD40L, IL-21, and IL-2 and treated with TCDD (10nM) or Veh (0.04% DMSO) as comparator for 7 days. On day 7 cells were collected and either surface stained for CD5 protein expression or assayed for IgM secretion by ELISPOT. The %IgM suppression for a given donor was calculated by normalizing each by the number of IgM+ spots in the TCDD-treated samples to the number of spots in each donors Veh control. A representative flow plot of CD19 expressing CD5+ B cells is shown in panel (A) CD5+ cells were identified in the lymphocyte, singlet gate by gating on live CD19+ cells. The %IgM suppression was then graphed against the frequency of CD5 expression and is shown in panel (B) A linear regression analysis was performed to calculate slope, best fit (R), and significance. Data are from 7 independent experiments assessing a total of 18 human donors.
