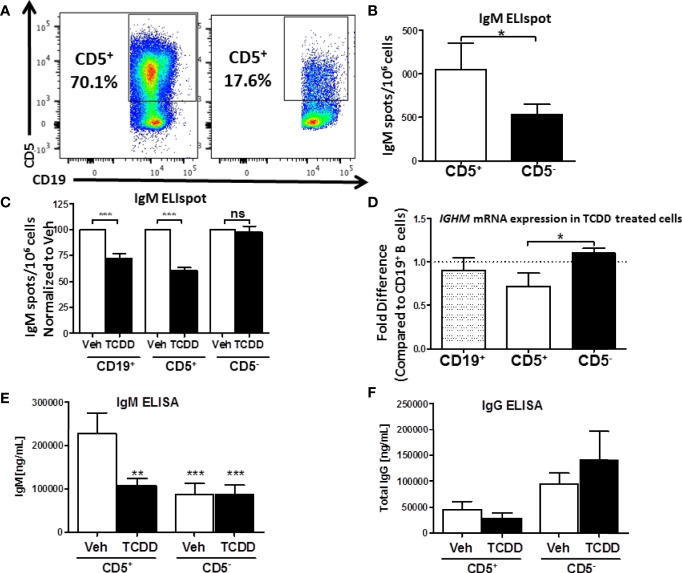
Figure 2.
Isolated CD5+ B cells secrete more IgM and less IgG compared to CD5- B cells and are preferentially sensitive to TCDD-mediated suppression of IgM secretion. CD19+ B cells were isolated from PBMC as previously described and then surface stained for 30 min with anti-CD5-PE antibody. Cells were then incubated with anti-PE biotin beads for 15 min, washed, incubated with strepavidin-ferous beads, and isolated by positive selection based on CD5 expression. Cells were then activated and treated as previously described or surface stained for CD19. Day 0 CD5+ and CD5- cell purity is shown in panel (A) Cells were gated on live, lymphocyte singlets. Activated CD5+ and CD5- cells were cultured for 7 days. After the culture period the relative number of IgM secreting cells was quantified by IgM ELISPOT (panel B). In treated cells, the percent suppression of IgM was calculated by normalizing IgM secretion in TCDD treated cells to each donor’s respective Veh control. For qRT-PCR analysis of IGHM mRNA, activated and treated cells were collected on Day 7, lysed, and RNA extracted. cDNA libraries were generated and qRT-PCR performed for IGHM and 18s. The ΔΔCt method was used to calculate relative expression of IGHM compared to total CD19+ B cells shown in (D) Secreted IgM and IgG in culture supernatants were quantified by anti-IgM and anti-IgG ELISAs which are shown in panel (E, F), respectively. A student’s t test was used to determine significance in (B) A one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s posttest was used to determine significance in (C–F) While not significant, the p values for comparison of CD19+ B cell IGHM mRNA to CD5+ and CD5- B cells were p=0.4128 and 0.2075, respectively. Results are from 6 independent experiments assessing a total of 17 human donors (B–D) or 4 experiments assessing a total of 8 human donors (E, F). ns = not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.