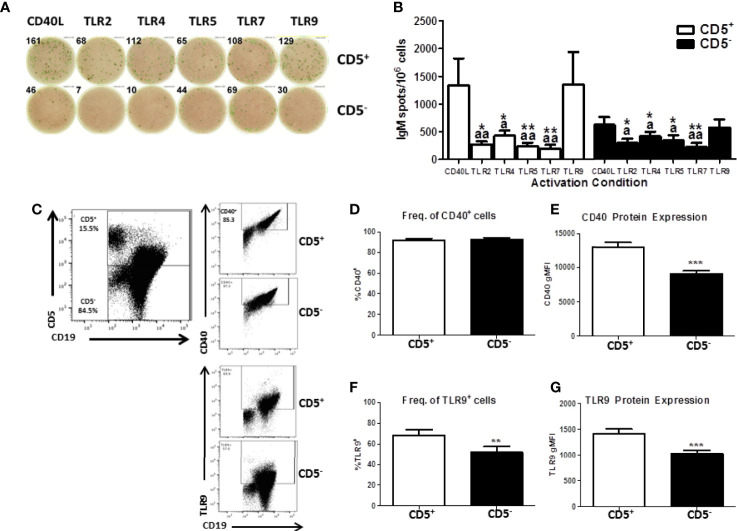
Figure 6.
Human CD5+ B cells respond to T-dependent and T-independent activators. Human CD19+ naïve B cells were isolated from PBMC and separated into CD5+ and CD5- populations as previously described. Cells were then activated with IL-21, IL-2, and either CD40L or indicated TLR agonist. After the 7-day culture period, cells were collected and IgM secretion assessed via IgM ELISPOT. For quantification of CD40 and TLR9, freshly isolated CD19+ B cells were stained for CD19, CD5, and CD40 surface expression. Cells were then fixed and permeabilized and stained intracellularly for TLR9. Representative ELISPOT wells from a given donor are shown in panel (A) Averaged results from 3 independent experiments assessing a total of 8 human donors are shown in panel (B) Representative flow plots showing CD5, CD40, and TLR9 are shown in panel (C) Averaged results from 2 independent experiments assessing a total of 9 human donors are shown in panels (D–G). A repeated measures ANOVA with a Tukey’s posttest was used to determine significance in panel B where * indicates significant differences compared to CD40L activation within each cell type. “a” indicates significant differences compared to TLR9 activation within each cell type. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ap < 0.05, and aap < 0.01. A paired t-test was used to determine significance in panels (D–G) where **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.