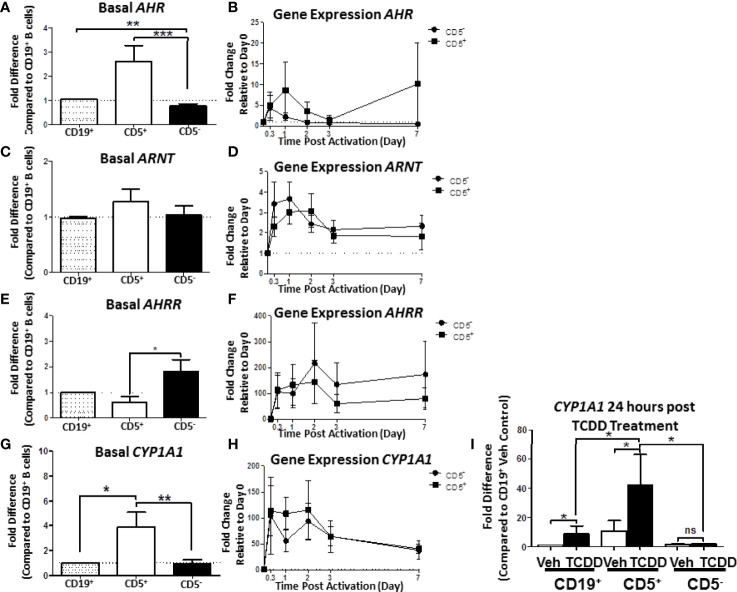
Figure 7.
Human CD5+ B cells express higher basal AHR and CYP1A1 and reduced basal AHRR compared to CD5- B cells. CD19+, CD5+, and CD5- B cells were isolated as previously described and either lysed for RNA extraction, activated, or treated with 10nM TCDD for 24 hours. Activated cells were collected at the indicated times, and cell pellets were stored at -80°C until RNA extraction. Cells treated with TCDD were lysed and RNA extracted after the 24-hour treatment. Extracted RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA libraries and the relative gene expression for AHR, ARNT, AHRR, and CYP1A1 was determined by qRT-PCR. For panels (A, C, E, G), relative gene expression was compared to CD19+ bulk B cells. In panels (B, D, F, H), relative gene expression was determined compared to Day 0. For panel (I), CYP1A1 gene expression was compared to CD19+ B cells treated with Veh. Results are from 3 independent experiments assessing a total of 8 human donors. Significance was calculated using a repeated measures ANOVA with a Tukey’s posttest. ns = not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.