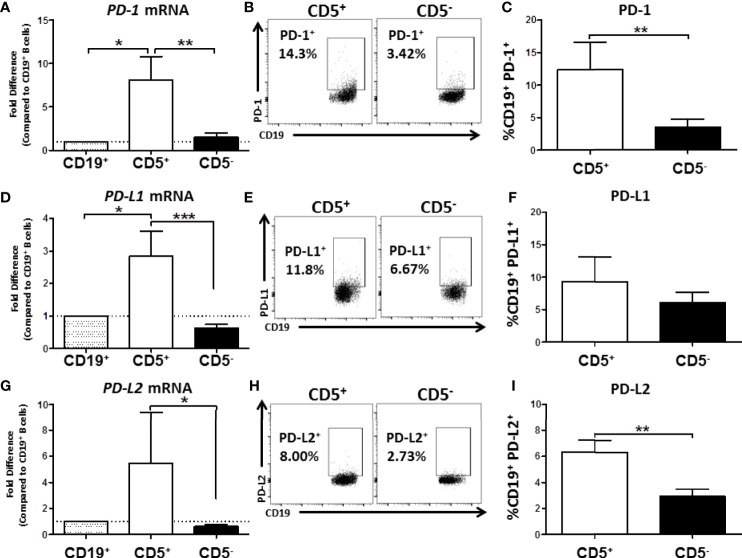
Figure 8.
Human CD5+ B cells express higher basal PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 compared to CD5- B cells. CD19+, CD5+, and CD5- B cells were isolated as previously described and either lysed for RNA extraction or surface stained for PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 protein expression directly ex vivo. Extracted RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA libraries and the relative gene expression for PDCD1, CD274 and PDCD1LG2 was determined by qRT-PCR. For panels (A, D, G) relative gene expression was compared to CD19+ bulk B cells. Representative flow plots for PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 protein expression is shown in panels (B, E, H). PD-1+, PD-L1+, and PD-L2+ cells were identified in the lymphocyte, singlet gate by gating on live CD19+ cells. Averaged results from 3 independent experiments assessing a total of 8 human donors for PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 is shown in panels (C, F, I). Significance was calculated using a repeated measures ANOVA with a Tukey’s posttest. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.