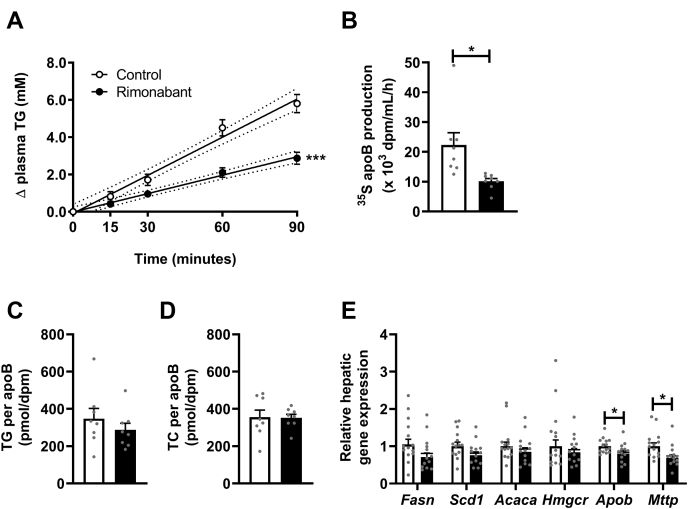
Fig. 3.
Rimonabant lowers hepatic VLDL-triglyceride (TG) and VLDL-ApoB production. Female APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP mice were fed a Western-type diet with or without rimonabant for 4 weeks. Mice received intravenous injection with Tran[35S] label followed by Triton WR1339, and TG levels were determined in plasma samples drawn at the indicated time points, which were (A) plotted as the increase in TG to baseline, from which VLDL-TG production rate was determined by linear regression. By measuring 35S in isolated VLDL (B), ApoB production rate was determined. C, D: VLDL lipid content was assessed and expressed as a ratio of ApoB. In 20-week treated mice, liver samples were collected to assess (E) relative mRNA expression levels of lipogenic (Fasn, Scd1, and Acaca) and cholesterogenic (Hmgcr) genes, as well as genes involved in VLDL assembly (Apob and Mttp). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and individual data points. ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Acaca, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; Fasn, fatty acid synthase; Hmgcr, HMG-CoA reductase; Mttp, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; TC, total cholesterol.