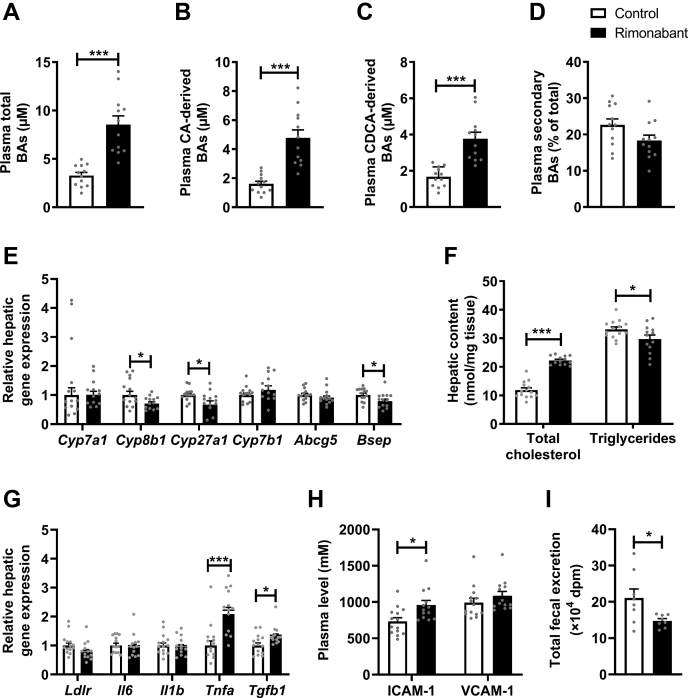
Fig. 4.
Rimonabant influences bile acid (BA) metabolism and hepatic cholesterol. Female APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP mice were fed a Western-type diet with or without rimonabant for 20 weeks. Mice were sacrificed, and heart puncture samples were collected to determine the plasma (A) total BAs, (B) cholic acid (CA)-derived BAs, and (C) chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA)-derived BAs, as well as (D) secondary BAs as a percentage of total. Liver samples were collected to assess (E) relative mRNA expression levels of genes involved in the classical BA synthesis pathway (Cyp7a1 and Cyp8b1), the alternative BA synthesis pathway (Cyp27a1 and Cyp7b1), and the excretion of neutral sterols and cholesterol (Abcg5 and Bsep), to assess (F) hepatic total cholesterol and TG content and to assess (G) expression of Ldlr and of various proinflammatory and profibrotic markers. H: In blood plasma collected after 20 weeks of treatment, plasma levels of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM-1) were determined. I: In an additional group of female APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP mice fed a Western-type diet with or without rimonabant for 2 weeks, mice received intraperitoneal injection with [3H]cholesterol-laden macrophages, and total fecal excretion of the radiolabel was determined during the following 72 h. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and individual data points. ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Abcg5, ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 5; Bsep, bile salt export pump; Cyp27a1, sterol 27-hydroxylase; Cyp7a1, cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase; Cyp7b1, oxysterol and steroid 7-alpha-hydroxylase; Cyp8b1, sterol 12-alpha-hydroxylase; Il6, interleukin 6; Il1b, interleukin 1 beta; Ldlr, low density lipoprotein receptor; Tgfb1, transforming growth factor beta 1; Tnfa, tumor necrosis factor alpha.